Urinary metabolomic profile and gastric cancer
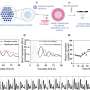
A research team from China investigated urinary metabolites expression changes among three mice groups using gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Ten metabolites have differences between the normal group and the cancer group (non-metastasis group and metastasis group). Furthermore, seven metabolites with characteristic expression levels were identified between non-metastasis group and metastasis group.
Metabolomics is a post-genomic research field for analysis of low molecular weight compounds in biological systems, and its approaches offer an analysis of metabolite level changes in biological samples. Recently, metabolomic method has shown great potentials in identifying the new diagnostic markers and therapeutic targets for cancers. However, metabolomic studies on cancer metastasis remain scarce.
A research article to be published on February 14, 2011 in the World Journal of Gastroenterology addresses this question. The authors used metabolomics, which is based on gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC/MS) technology, to study the urinary metabolites expression changes among three mice groups.
This is the first report on urinary metabolomic investigation in gastric cancer using GC/MS. Biomarkers discovered in this study are mainly low molecular weight metabolites, which are difficult to detect by traditional methods. On the basis of this research, the authors believe that urinary metabolomic information investigated by GC/MS might play a significant role in early diagnosis and screening metastasis or recurrence of gastric cancer.
More information: Hu JD, Tang HQ, Zhang Q, Fan J, Hong J, Gu JZ, Chen JL. Prediction of gastric cancer metastasis through urinary metabolomic investigation using GC/MS. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(6): 727-734 www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i6/727.htm