Noninvasive brain stimulation helps curb impulsivity
Inhibitory control can be boosted with a mild form of brain stimulation, according to a study published in the June 2011 issue of Neuroimage, Elsevier's Journal of Brain Function. The study's findings indicate that non-invasive intervention can greatly improve patients' inhibitory control. Conducted by a research team led by Dr Chi-Hung Juan of the Institute of Cognitive Neuroscience, National Central University in Taiwan, the research was sponsored by the National Science Council in Taiwan, the UK Medical Research Council, the Royal Society Wolfson Merit Award, and a Fulbright Award.
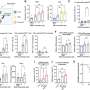
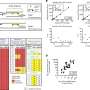
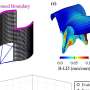
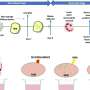
The study demonstrates that when a weak electrical current is applied over the front of participants' scalps for ten minutes, it greatly improved their ability to process responses – effectively jumpstarting the brain's ability to control impulsivity. The treatment has the potential to serve as a non invasive treatment for patients with conditions such as attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), Tourette's syndrome, drug addictions, or violent impulsivity.
Professor Chi-Hung Juan who led the research team noted, "The findings that electrical stimulation to the brain can improve control of their behavioral urges not only provide further understanding of the neural basis of inhibitory control but also suggest a possible therapeutic intervention method for clinical populations, such as those with drug additions or ADHD, in the future".
More information: Modulating inhibitory control with direct current stimulation of the superior medial frontal cortex. NeuroImage (2011). Tzu-Yu Hsu, Lin-Yuan Tseng, Jia-Xin Yu, Wen-Jui Kuo, Daisy L... Hung, Ovid J.L. Tzeng, Vincent Walsh, Neil G. Muggleton and Chi-Hung Juan. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.03.059