Ultrasound model IDs residual joint inflammation in RA
(HealthDay)—A model including ultrasound (US) assessment of the wrist, metacarpophalangeal (MCP), ankle, and metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joints is highly sensitive for detecting B-mode and Doppler joint inflammation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), according to a study published in the April issue of Arthritis Care & Research.
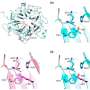
Esperanza Naredo, M.D., from the Hospital General Universitario Gregorio Marañón in Madrid, and colleagues recruited 67 patients with RA in clinical remission and treated with methotrexate to investigate the sensitivity of detecting subclinical synovitis of different reduced joint US assessment models compared with a comprehensive US assessment. Participants underwent evaluations for disease activity based on the Disease Activity Score in 28 joints (DAS28) and the Simplified Disease Activity Index (SDAI), as well as 44-joint B-mode and power Doppler (PD) assessment. At each joint, B-mode synovial hypertrophy (SH) and synovial PD signal were assessed.
The researchers found that the highest correlations with the comprehensive US assessment were seen for wrist, second through fifth MCP, ankle, and second through fifth MTP joint, as well as the 12-joint US assessments. Compared with the comprehensive US assessment, the wrist, MCP, ankle, and MTP joint assessment exhibited the highest sensitivity for detecting SH and synovial PD signal for patients in remission, based on DAS28 and SADI criteria.
"The results of this cross-sectional study suggest that US assessment of wrist, MCP, ankle, and MTP joints can be highly sensitive for detecting B-mode and Doppler joint inflammation in RA patients in clinical remission," the authors write.
More information:
Abstract
Full Text (subscription or payment may be required)
Health News Copyright © 2013 HealthDay. All rights reserved.