Identifying a mystery channel crucial for hearing
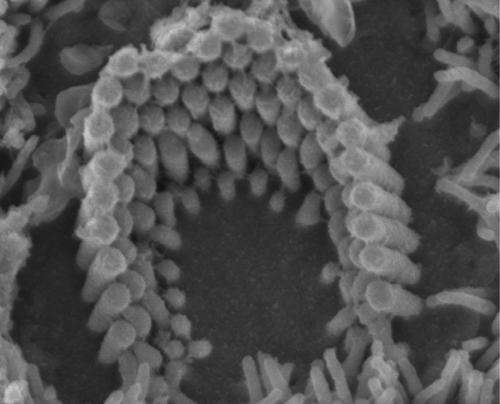
Our ability to hear relies on hair cells, sensory receptors that mechanically amplify low-level sound that enters the inner ear through a transduction channel. Although the transduction channel was characterized more than 30 years ago, researchers have been unable to identify its molecular components. A new study in The Journal of General Physiology could help lead to a definitive identification of this mystery channel.
Recent studies have suggested that members of the TMC family of membrane proteins are strong candidates as the components of the hair cell's transduction channel. Now, a team led by scientists from the University of Wisconsin Medical School provides evidence that the TMCs instead couple the transduction channel to tip links—the mechanical elements that provide directional sensitivity to hair cells—and are not the channel itself. This suggests that the transduction channel may be a membrane protein distinct from TMCs that only functions properly once other key molecules are expressed.
Whether or not TMCs turn out to be the transduction channel, the new results affirm that they play a central role in hair cell mechanotransduction. The work adds to evolving research aimed at understanding the cellular and molecular mechanisms that affect hearing.
More information: Barr-Gillespie, P.G., and T. Nicolson. 2013. J. Gen. Physiol DOI: 10.1085/jgp.201311111 Kim, K.X., et al. 2013. J. Gen. Physiol. DOI: 10.1085/jgp.201311068