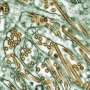
Propranolol, doxycycline combo safe, effective in rosacea

(HealthDay)—For patients with rosacea, combination treatment with propranolol and doxycycline is effective and safe, according to a study published in the January issue of the Journal of Dermatology.
Jung-Min Park, from Pusan National University in Busan, South Korea, and colleagues conducted a comparative study of propranolol, doxycycline, and combination therapy using both in 78 patients with rosacea. Twenty-eight patients were treated with propranolol, 22 with doxycycline, and 28 with the combination of propranolol and doxycycline.
The researchers found that in all groups there was improvement from baseline in the patient global assessment and investigator global assessment; during the entire period, combination therapy was most effective, but the difference was not statistically significant. The combination group had the highest reduction rate of assessment of rosacea clinical score (57.4 percent versus 52.2 percent for doxycycline and 51.0 percent for propranolol). Mild and transient gastrointestinal disturbances were seen in three patients in the combination group, but the difference was not significant when compared with the other groups.
"We conclude that the combination therapy of doxycycline and propranolol is [an] effective and safe treatment for rosacea and successful for reducing both flushing and papulation in particular," the authors write.
More information:
Abstract
Full Text (subscription or payment may be required)
Copyright © 2015 HealthDay. All rights reserved.