Unassuming 'Swiss Army knife'-like protein key to new cancer drug's therapeutic action
When preliminary tests show that a new drug has remarkable effectiveness against a lethal illness, everyone wants to know how it works. Often, a mechanism of action is hard to pin down, but when it can be, a candidate drug's chances increase. Knowing how it works sometimes means you can figure out ways to enhance its effectiveness or take another tack if patients develop resistance to it.
Today in the journal Molecular Cell, a team of researchers at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) reports a surprising mechanism through which an important new candidate drug against leukemia exerts its therapeutic effect. The drug, called JQ1, is expected to soon enter the second phase of human clinical trials. But in animal models of AML (acute myeloid leukemia), an often deadly blood-cell cancer, JQ1 has brought about dramatic reversals in disease progress.
CSHL Associate Professor Christopher Vakoc in 2011 performed genetic screens that brought to light a powerful target against which to direct an anti-AML drug. The target is BRD4, a seemingly unremarkable member of a family of proteins called transcriptional coactivators, which help initiate gene expression. Vakoc's team showed that in AML, cancer cells require BRD4 in order to proliferate out of control. JQ1, a drug then in early stages of development for other purposes, was found by Vakoc to inhibit BRD4 and generate powerful toxic effects. The drug, importantly, did not harm normal cells, but devastated cancer cells in the AML type of leukemia.
In the lab's latest work, graduate student Chen Shen led a rigorous series of experiments culminating in the surprising discovery of how a BRD4-inhibiting drug like JQ1 undermines AML cells. Because BRD4 was known to impact gene expression by affecting the deposition of chemical tags on DNA called epigenetic marks, Shen examined other molecular players - other proteins - that might also be in involved with BRD4 in epigenetic processes in AML cells.
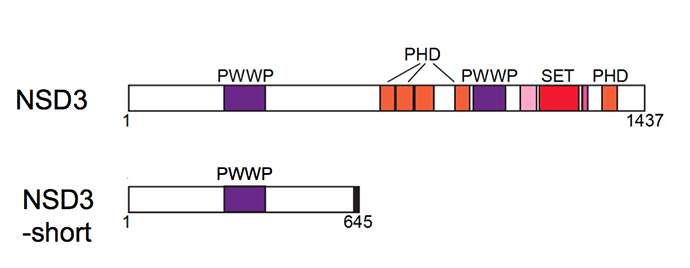
Among the proteins she studied was an enzyme called NSD3. Like many proteins in our cells, this one comes in multiple forms, one rather long and another quite short. "It's a David-and-Goliath story," explains Vakoc. "We figured the long, or full-length, form of NSD3 was of interest because it has a portion, or domain, that enables it to act as an enzyme, and another that suggests its involvement in epigenetic gene regulation."
In fact, though, researcher Chen was able to prove that it was not this Goliath, but rather David—a highly truncated version of NSD3 called NSD-short - that was relevant to BRD4, and, indeed, the action of a BRD4-inhibiting drug like JQ1.
"Chen found NSD3-short, despite its very unimpressive appearance, is critical," says Vakoc. "It's like a short strip of Velcro, and BRD4 sticks to one portion of it, while another protein called CHD8 sticks to another portion. We call it an adaptor protein."
Chen and Vakoc discovered that when JQ1 is applied to AML cells, it causes a 3-protein complex consisting of NSD3-short, BRD4 and CHD8 "to fly apart." The Velcro is no longer sticky.
Serving as an adaptor for others is only one of multiple functions the seemingly modest NSD3-short protein performs. "There are four different ways this protein enables AML cells to do what they do," says Vakoc. "All are necessary for the cancer to thrive. So you can think of it as a kind of Swiss Army knife with four blades, all of which are needed to activate a cancer cell."
One way is to attract and bind BRD4; a second is to attract and bind CHD8. A third is to "read" epigenetic marks. A fourth is the protein's ability to activate genes, via a portion called an acidic activation domain.
Cancer cells exploit a great number of molecular players in order to commandeer growth and steer cells out of control. The target Vakoc's team discovered four years ago, BRD4, is like an Achilles' heel for at least one specific cancer, AML. Now, the new work by Chen "draws another bullseye for future drug discovery," Vakoc says. The NSD3 protein has already been identified as important in the pathologies of certain kinds of breast and lung cancers. It is therefore possible that a future drug targeting NSD3-short or CHD8, the other protein that sticks to it, might have therapeutic effects not only in AML but perhaps also breast, lung and other cancer types.
More information: "NSD3-short is an adaptor protein that couples BRD4 to the CHD8 chromatin remodeler" appears December 3, 2015 in Molecular Cell.