Candy games stimulate appetite
At least once a week, two thirds of all children of primary-school age will play an internet game that was created to draw attention to a brand. Most of these advertisements are for snacks and candy. Only 6% of these children are aware that such advergames are advertisements. In the meantime, such games do affect their behaviour, discovered Frans Folkvord, and if it were up to him they would be banned. Folkvord, a behavioural scientist at Radboud University, will be awarded a PhD for his work on 13 January 2016.
Good news for marketers, bad news for anyone concerned about the increase of unhealthy eating behaviour amongst children: shortly after playing a game with an embedded food advertisement, children ate 55% more of the candy offered to them than children who had played a game with an embedded toy advertisement. Frans Folkvord tested the effects of such hidden online food advertisements on the eating behaviour of more than 1000 children.
Not clear that it is advertising
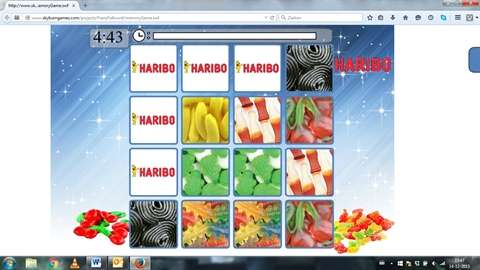
"In contrast to television, where the clearly delimited blocks of commercials can help viewers guard against temptation, on the internet, advertising is mixed with other types of content. The websites of food manufacturers contain games, which also offer children the option of sharing games with their friends."
Folkvord discovered that children do not recognise the games as advertisements, even when brand names and logos are clearly visible. Moreover, it does not matter whether the games are about candy or fruit: children eat more candy after playing a game involving food. During the five-minute break after playing the food-related games, children ate 72 more calories (16 M&Ms or 10 candy cola bottles) than did children in the control conditions.
Heavier children are more sensitive to food advertising
Although Folkvord found no link between eating candy and having a higher BMI two years later, choosing the snack did have an effect. According to Folkvord's results, the BMIs of children who chose to satisfy their hunger with an apple instead of with candy were lower two years later than were those of children who had chosen to satisfy their hunger with candy. "These children had apparently learned to make healthier choices."
Folkvord argues the necessity of a discussion concerning the prohibition of food commercials aimed at children. He is collaborating with the University of Barcelona to formulate a recommendation to the European Union in this regard. "Children play a game, get hungry and reach for treats. As the cycle continues, children fail to learn healthy eating behaviour. The results of my study indicate that these advertisements have an even heavier influence on children who are already overweight."
Overview study on food marketing to children
In a review study published last week (8 December), Frans Folkvord and other authors, including his supervisor Professor Moniek Buijzen, list and evaluate the literature on marketing to children and eating behaviour. Amongst other revelations, the review indicates that manufacturers' promises to decrease their advertising to children are of no value. "That is all the more reason to advocate a ban."
More information: Frans Folkvord et al. Food advertising and eating behavior in children, Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences (2016). DOI: 10.1016/j.cobeha.2015.11.016