WHO approves new, faster treatment for drug-resistant TB
The World Health Organization approved a new treatment for multi-drug resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) on Thursday, a crucial step towards replacing an old, costly therapy that is brutal on patients and only 50-percent effective.
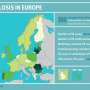
An estimated 480,000 people contract MDR-TB each year, accounting for roughly five percent of the 9.6 million TB cases recorded annually worldwide.
Unlike simple tuberculosis, MDR-TB has proved extremely difficult to treat, requiring patients to take painful injections and thousands of pills over a period of 18-24 months, often with devastating side effects, including deafness in some cases.
The old MDR-TB treatment regimen "is pretty much a tragedy," said Mario Raviglione, the head of WHO's TB programme, noting the 50 percent success rate.
The new regimen, which WHO will now encourage all its member-states to adopt, lasts up to nine months, easing the burden on patients and possibly curing more than 80 percent of cases.
But it does not include newly-discovered drugs. Instead, it is made up of a cocktail of existing medication, including one repurposed drug originally used to treat leprosy.
The treatment process is also cheaper, possibly costing as little as $400 (350 euros) per patient, compared to the $1,500-$3,000 under the old regimen, Raviglione told reporters.
"This is a critical step forward," he said.
Not enough research
Roughly 30 percent of MDR-TB patients infected with an especially complicated form of the disease will not be able to benefit from the new treatment regimen, because of added drug resistance.
To identify a patient's eligibility for the shorter therapy, the UN's health agency also approved the use of a new diagnostic test which identifies the precise nature of a TB infection within 48 hours. Previous testing took up to three months.
TB is a bacterial disease that mostly infects the lungs and kills an estimated 1.5 million people per year, mostly in low and middle income countries.
An estimated 190,000 people die from MDR-TB every year.
Despite the threat, there has been little investment and research aimed at improving treatment, said I.D. Rusen, vice president of the Union against Tuberculosis and Lung Disease, which helped develop the new regimen.
"TB hasn't received the attention and profile it deserves," he said, noting that two billion people—roughly a third of the world's population—have a latent form of TB in their system.
Raviglione agreed, telling reporters that MDR-TB patients were for years confined to a brutal treatment regimen in part because drug companies devote scant resources to TB research.
© 2016 AFP