Amyloid study pinpoints protein culprits

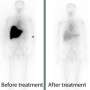
A five-year trial at a Brisbane Hospital has increased the accuracy of diagnosing patients with amyloidosis, a group of rare and incurable diseases caused by abnormal protein deposits in tissues and organs.
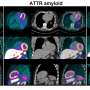
Researchers from The University of Queensland and the Princess Alexandra Hospital Amyloidosis Centre used a new test to identify the specific protein that caused the damage in each patient.
Associate Professor Michelle Hill from the UQ Diamantina Institute said different amyloid conditions had different protein culprits, and required different treatments.
"For instance, in one type of amyloidosis known as AL, chemotherapy is required, but chemo is inappropriate and potentially harmful to patients with other amyloid conditions," Dr Hill said.
"In the trial we used cutting-edge techniques including laser-capture microdissection and tandem mass spectrometry to identify proteins in the amyloid deposits.
"This technique was recently reported by the Mayo Clinic in the United States as a new diagnostic tool for amyloidosis, but it has not yet been evaluated in other centres.
"It is a challenging technique because of the small size of the protein deposits and the technical skills required for the multiple steps of the method.
"We were pleased to be able to identify amyloid proteins in 121 out of 131 attempted cases in this study, a success rate of 92 per cent."
The PAH Amyloidosis Centre is the only centre in Australia to provide mass spectrometry analysis for amyloidosis patients.
Centre Director Dr Peter Mollee said the assay's accuracy was a significant improvement on traditional laboratory tests.
"We tested previous methods on a subset of the samples from this study and the success rate was only 45 per cent," Dr Mollee said.
"Strikingly, during the course of the five-year trial, the mass spectrometry assay results altered the diagnosis in almost a quarter of all cases.
"This is a big step forward for amyloid patients because identifying the culprit protein is so important to delivering the right treatment."
More information: Peter Mollee et al. Implementation and evaluation of amyloidosis subtyping by laser-capture microdissection and tandem mass spectrometry, Clinical Proteomics (2016). DOI: 10.1186/s12014-016-9133-x