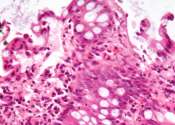
Specific bacterium in the gut linked to irritable bowel syndrome
Researchers at the University of Gothenburg have detected a connection between Brachyspira, a genus of bacteria in the intestines, and IBS—especially the form that causes diarrhea. Although the discovery needs confirmation ...
Nov 25, 2020
0
78