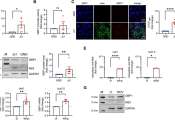
Canada likely to miss WHO's hepatitis C elimination target, research shows
Canada will not reach the original World Health Organization's (WHO) target of eliminating the hepatitis C virus (HCV) by 2030 and lags in comparison to other developed countries, a new study led by researchers at the University ...
Apr 15, 2024
0
3