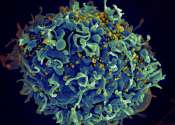
Researchers identify a new HIV reservoir
HIV cure research to date has focused on clearing the virus from T cells, a type of white blood cell that is an essential part of the immune system. Yet investigators in the Division of Infectious Diseases at the University ...
Apr 17, 2017
0
203