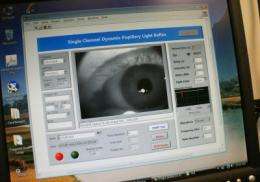
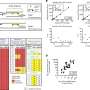
The computerized binocular infrared pulillography device produces a movie and other data that demonstrate how the eye's pupil reacts to a flash of light. Credit: University of Missouri
Autism affects 1 in 150 children today, making it more common than childhood cancer, juvenile diabetes and pediatric AIDS combined. Despite its widespread effect, autism is not well understood and there are no objective medical tests to diagnose it. Recently, University of Missouri researchers have developed a pupil response test that is 92.5 percent accurate in separating children with autism from those with typical development. In the study, MU scientists found that children with autism have slower pupil responses to light change.
"No comprehensive study has been conducted previously to evaluate the pupils' responses to light change, or PLR, in children with autism," said Gang Yao, associate professor of biological engineering in the MU College of Agriculture, Food and Natural Resources and the College of Engineering. "In this study, we used a short light stimulus to induce pupil light reflexes in children under both dark and bright conditions. We found that children with autism showed significant differences in several PLR parameters compared to those with typical development."
In the study, scientists used a computerized binocular infrared device, which eye doctors normally use for vision tests, to measure how pupils react to a 100-millisecond flash light. A pupil reaction test reveals potential neurological disorders in areas of the brain that autism might affect. The results showed that pupils of children diagnosed with autism were significantly slower to respond than those of a control group.
"There are several potential mechanisms currently under study," Yao said. "If these results are successfully validated in a larger population, PLR response might be developed into a biomarker that could have clinical implications in early screening for risks of autism. Studies have shown that early intervention will improve these children's developmental outcome."
Source: University of Missouri-Columbia (news : web)