'Locked-in' patients happier than thought - study
Many people with "locked-in" syndrome, in which they are conscious but completely paralysed, indicate they are happy, a finding with repercussions for assisted suicide, European doctors reported on Wednesday.
Investigators asked 168 members of the French Association for Locked-in Syndrome (ALIS) about their medical history, emotional state and quality of life, with the responses noted by caregivers.
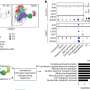
Of those who replied in full, 72 percent said they were happy and 28 percent said they were unhappy. Four percent said they wanted to opt for suicide.
Many of those who described themselves as unhappy said they had been locked-in for less than a year, had bouts of anxiety and suffered from the lack of mobility and crimp on social and recreational activities.
The researchers admit that the results could be skewed by a low response rate.
Only 91 patients of the 168 responded, and out of these, 26 questionnaires lacked information about the quality of life, which left only 65 full replies.
Even so, the authors argue that the findings contribute to a powerful debate in Europe as to whether assisted suicide should be made available to locked-in patients on the assumption that their life is intolerable.
Locked-in syndrome is the term for a condition in which the patient is fully conscious but cannot move or communicate, except through eye movements or blinking, after suffering damage to the brain stem.
In some cases, speech and control of the head, fingers or feet can be recovered. More than 80 percent of patients with locked-in syndrome survive 10 years, and some live on for decades.
"Our data show that, whatever the physical devastation and mental distress of patients during the acute phase of the condition, optimal life sustaining care and revalidation can have major long-term benefit," says the paper.
"We suggest that patients recently struck by (the syndrome) should be informed that, given proper care, they have a considerable chance of regaining a happy life."
Requests for assisted suicide "are only valid when the patients have been given a chance to attain a steady state of subjective wellbeing."
The study, led by Steven Laureys, a professor of neurology at the University of Liege in Belgium, appears in an online journal, BMJ Open, published by the British Medical Association (BMA).
Of the 91 patients who replied, two-thirds had a partner and lived at home, and 70 percent of them had religious beliefs.
(c) 2011 AFP