Scientists identify KRAS rearrangements in metastatic prostate cancer
Scientists have uncovered a genetic characteristic of metastatic prostate cancer that defines a rare sub-type of this disease. These findings are published in Cancer Discovery, the newest journal of the American Association for Cancer Research, which will debut at the AACR 102nd Annual Meeting 2011, held April 2-6.
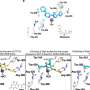
Arul M. Chinnaiyan, M.D., Ph.D., an investigator of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute and director of the Michigan Center for Translational Pathology, and colleagues identified an oncogenic gene fusion of KRAS, one of the most studied and well-known oncogenes in a metastatic prostate cancer cell line.
Like most metastatic disease, metastatic prostate cancer has a grim prognosis. As scientists learn more about the genetic characteristics of this disease, they may be able to work backward and accurately predict which early-stage prostate cancers will be more aggressive and thus require additional therapy and management.
"Right now, we can identify the presence of prostate cancer but not accurately predict which of these cancers will have a poor prognosis," said Chinnaiyan. "Although prostate cancer is a leading cause of cancer-related death, we need better prognostic information to separate the slow growing tumors from the more aggressive ones."
Chinnaiyan compared the identification of the KRAS gene in metastatic prostate cancer to the work that has been previously done in breast cancer, where scientists now recognize that breast cancer comes in multiple subtypes and requires different treatment strategies.
"The more we know about the disease biologically, the better we'll be able to treat it," said Chinnaiyan.
Currently, there are no treatments that block the KRAS oncogene, but several are under development that target components of the KRAS signaling pathway.