New University of Otago research suggests that a stronger focus is needed on preventing accidental nerve injury during medical treatments in New Zealand.
In the first study of its kind in this country, Department of Anatomy researchers analysed 5227 treatment injury claims accepted by the Accident Compensation Corporation of New Zealand (ACC) in 2009.
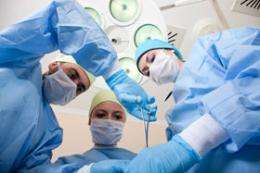
The research, led by PhD student Abigail Moore and Professor Mark Stringer, identified 313 ACC claims involving inadvertent nerve injuries occurring during medical treatment and diagnosis. They found that two-thirds of these occurred in patients undergoing surgery.
Ms Moore says the research found that the most common cause of nerve injury was when a patient was incorrectly positioned on the operating table under general anaesthesia. Other situations in which nerve injury occurred commonly were when drawing blood for testing and during hip replacement.
“Many of these injuries are minor with no persistent symptoms, but sometimes they cause pain and paralysis and can be very distressing, says Ms Moore. Over a quarter of patients were delayed from getting back to work by the injury, and about 1 in 10 were referred to a surgeon for treatment.”
Accidental nerve injuries happen in all modern healthcare systems and not all such injuries are avoidable, but many could be prevented by greater awareness of which nerves are damaged and in what procedures, she says.
The findings are recently published in the International Journal of Clinical Practice.
Provided by University of Otago