White matter of abstinent alcoholics recovers over time
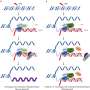
(HealthDay) -- Based on diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), the microstructural changes seen in the genu and body of the corpus callosum in recently detoxified alcohol-dependent patients are found to improve after one year of abstinence, according to research published online May 2 in Alcoholism: Clinical & Experimental Research.
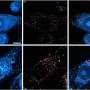
Omar M. Alhassoon, Ph.D., of the University of California in San Diego, and colleagues used DTI to compare 15 recently detoxified alcohol-dependent male patients and 15 age- and education-matched nonalcoholic controls. The comparisons were made after two weeks and after one year of alcohol abstinence by the alcohol-dependent patients.
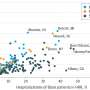
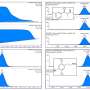
The researchers found that, compared with controls, after two weeks of abstinence, significantly lower fractional anisotropy and greater radial diffusivity were seen in the genu and body of the corpus callosum of the recently detoxified alcohol-dependent patients. After one year there was a significant time by group interaction, with fractional anisotropy increasing and radial diffusivity decreasing in these two regions in patients but not in controls. There were no improvements seen between the two time points in a smaller relapse group.
"The results suggest susceptibility of the genu and body of the corpus callosum to the effects of alcohol, and the potential for recovery of both these regions after abstinence, perhaps via mechanisms involving myelin reconstitution," the authors write.
More information:
Abstract
Full Text (subscription or payment may be required)
Copyright © 2012 HealthDay. All rights reserved.