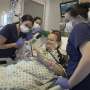
University Hospitals (UH) Case Medical Center is one of five institutions nationwide performing a novel scarless procedure that restores swallowing function in some patients with achalasia, a rare condition where the esophagus is unable to move food into the stomach. Per-oral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) is a state-of-the-art technique to treat patients without any external incisions or outside scars. With POEM, surgeons enter through the mouth and tunnel an endoscope down the esophagus to cut the muscle fibers to open the esophagus, allowing food to enter the stomach.
"The POEM procedure provides a more minimally invasive approach to achalasia that will help patients recover more quickly," says Jeffrey L. Ponsky, MD, Chairman of the Department of Surgery at UH Case Medical Center and Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine. "This leading-edge surgery is the way of the future."
UH Case Medical Center has successfully performed 15 POEM surgeries and continues to enroll appropriate candidates into a clinical trial of POEM. About 700 POEM procedures have been done worldwide, estimates Jeffrey Marks, MD, Director, Surgical Endoscopy, UH Case Medical Center; and Professor, Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine.
University Hospitals Case Medical Center in Cleveland, OH, is one of five institutions nationwide performing a novel scarless procedure that restores swallowing function in some patients with achalasia, a rare condition where the esophagus is unable to move food into the stomach. Per-oral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) is a state-of-the-art technique to treat patients without any external incisions or outside scars. Credit: Jennifer Guerrieri, University Hospitals Case Medial Center News Service
The POEM procedure was developed two years ago in Japan, using refined technologies and approaches learned from natural orifice translumenal endoscopic surgery (NOTES). NOTES is a technique to remove organs using the body's natural orifices as an entry point.
While the scarless procedure is being pioneered in patients with achalasia, this approach has potential applications for multiple other gastrointestinal diseases. Tunneling techniques like those used in POEM and NOTES are developing rapidly as surgeons see that they are well-tolerated by the body.
"As we continue to learn about tunneling techniques and develop new tools, we're increasingly optimistic about what this means for the future of surgery," says Dr. Marks, who likened POEM to the advent of laparoscopic surgery. "Within the last two decades, laparoscopy transitioned from a revolutionary medical advancement to a commonplace procedure. We're hopeful that in the future we can apply methods like POEM to other areas."
More than 3,000 people are diagnosed with achalasia each year. The most common symptom is difficulty swallowing. Because patients have trouble eating and drinking, achalasia can lead to unintentional weight loss and malnutrition.
Traditional methods to treat achalasia include pharmacologic therapy, surgical therapy and endoscopy therapy. Surgical cure initially was done with a procedure called a Heller myotomy. In recent years, surgeons have performed the procedure laparoscopically, with about five small incisions in the abdomen.
POEM provides a number of benefits over traditional treatment methods, including faster patient recovery, the ability to avoid abdominal surgery and outside scarring, a potential reduced risk of reflux problems, a decreased chance of disrupting other tissues and greater surgical precision. It is a particularly beneficial approach for patients who would be more of a challenge to treat surgically because of prior esophageal or stomach operations or for patients who are morbidly obese.
Provided by University Hospitals Case Medical Center