U.S. obstetricians are getting more precise about exactly what determines a full-term pregnancy.
On average, a pregnancy lasts 40 weeks, counting from the first day of the woman's last menstrual period. That's how a due date is estimated.
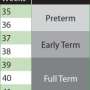
A baby is considered preterm if he or she is born before 37 weeks of pregnancy. Until now, a "term" baby was defined as one born anytime from 37 weeks to 42 weeks, a few weeks before or after the calculated due date.
Now the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists is refining the definition of a term pregnancy to make clear that even at the end of the last trimester, a little more time in the womb can be better for a baby's health and development.
"Weeks matter," said Dr. Jeffrey Ecker of Massachusetts General Hospital, who chaired the ACOG committee that came up with the more specific labels. Since babies' outcomes can differ, "let's not call it all the same."
The new definitions, released Tuesday in the journal Obstetrics & Gynecology:
—Early Term, between 37 weeks and 38 weeks 6 days.
—Full Term, between 39 weeks and 40 weeks 6 days.
—Late Term, the 41st week.
—Post Term, after 42 weeks.
In recent years, doctors' groups and the March of Dimes charity have stressed that elective deliveries—inductions and C-sections scheduled without a medical reason—shouldn't happen before the 39th week of pregnancy. Research shows that babies born at 37 weeks have more of a risk of complications, such as difficulty breathing, than those born just two weeks later.
Ecker said the new definitions will help doctors communicate that message.
© 2013 The Associated Press. All rights reserved.