(HealthDay)—Afternoon moderate-to-vigorous physical activity (MVPA) increases the risk of overnight and next-day hypoglycemia in adolescents with type 1 diabetes, according to research published in the May issue of Diabetes Care.
Kristen M. Metcalf, M.D., of the University of Iowa in Iowa City, and colleagues assessed the acute temporal associations between MVPA and hypoglycemia in 19 participants (53 percent female) aged 14 to 20 years with type 1 diabetes. The researchers used logistic regression models, adjusted for sex, percent body fat, fitness, and concurrent MVPA, to estimate the likelihood of nighttime and next-day hypoglycemia due to MVPA.
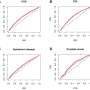
The researchers found that the participants were of average fitness and adiposity, and a majority (63.2 percent) met the national U.S. guideline of engaging in 60 minutes per day of MVPA. Among those who accumulated 30 minutes per day more MVPA in the previous afternoon, compared with those who accumulated less MVPA, hypoglycemia was 31 percent more likely (95 percent confidence interval, 1.05 to 1.63; P = 0.017).
"While promoting physical activity as a healthy behavior, it is important to educate adolescents with type 1 diabetes on prevention of hypoglycemia following physical activity," the authors write.
One author disclosed financial ties to Daiichi Sankyo.
More information:
Abstract
Full Text (subscription or payment may be required)
Journal information: Diabetes Care
Copyright © 2014 HealthDay. All rights reserved.