Connecting sleep deficits among young fruit flies to disruption in mating later in life
Mom always said you need your sleep, and it turns out, she was right. According to a new study published in Science this week from researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, lack of sleep in young fruit flies profoundly diminishes their ability to do one thing they do really, really well – make more flies.
The study, led by Amita Sehgal PhD, professor of Neuroscience and a Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI) Investigator, links sleep disruption in newborn fruit flies with a critical adult behavior: courtship and mating.
The team, addressed sleep in the very youngest of flies. "These flies sleep considerably more than adults and that behavior repeats across the animal kingdom," Sehgal says. "Infant humans, rats, and flies, they all sleep a lot."
Co-author Matthew Kayser, MD, PhD, in the Department of Psychiatry and Center for Sleep and Circadian Neurobiology, whose research centers on the link between sleep disruption and human neuropsychiatric diseases, used the fly – which is far more genetically pliant than mammals—to ask two basic questions: Why do young animals sleep so much? And, what is the implication of altering those patterns?
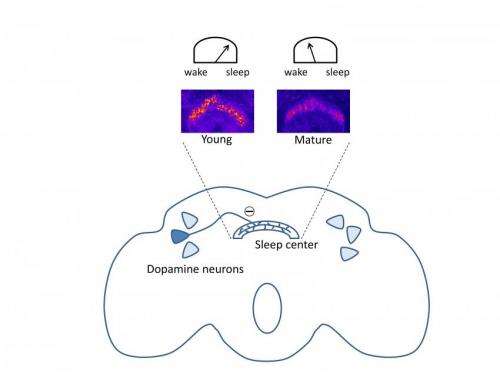
The team used genetically manipulated flies to show that young flies normally produce relatively little dopamine – a wake-promoting neurotransmitter—in certain neural circuits that feed into the sleep-promoting brain region called the dorsal fan-shaped body (dFSB). Premature activation of those circuits profoundly inhibits the dFSB, reducing sleep.
That answers the first question, Sehgal explains: Young flies make less dopamine, which keeps the dFSB active and sleep levels high. These animals sleep more than adults and are harder to rouse from sleep.
Some clues to the second question – what is the consequence of sleep loss – came from Kayser's finding that increased dopamine in young flies not only causes sleep loss, but also affects their ability to court when they're older. "The flies spend less time courting, and those that do usually don't make it all the way to the end," Sehgal says.
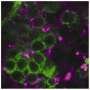
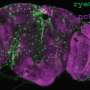
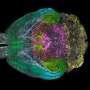
To address whether sleep loss in young flies affects development of courtship circuits, the team investigated a group of neurons implicated in courtship. One particular subset of those neurons, localized in a specific brain region called VA1v, was smaller in sleep-deprived animals than normal flies, suggesting a possible mechanism for how sleep deprivation can lead to altered courting behavior.
That sleep-deprived flies have altered behavior is not itself a novel finding, Sehgal notes. Earlier studies from her lab and others used mechanical disruption to alter sleep patterns, but in the current study, Sehgal's team was able to drill down to the specific neural network that is affected. "We identified the circuit that is less active in young flies. If you activate that circuit, you disrupt courtship by impairing the development of a different, courtship-relevant circuit."
The question now is how these findings relate to human behavior – Kayser's original question. Though no direct lines can be drawn, the study "does provide the first mechanistic link between sleep in early life and adult behavior," says Sehgal.
More information: "A Critical Period of Sleep for Development of Courtship Circuitry and Behavior in Drosophila," by M.S. Kayser et al. Science, 2014.