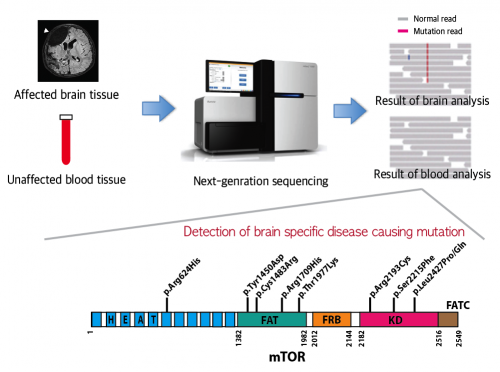
A schematic image shows how to detect brain specific mutations using next-generation sequencing technology with blood-brain paired samples. Simple comparison of non-overlapping mutations between affected and unaffected tissues is able to detect brain specific mutations. Credit: KAIST
Epilepsy is a brain disorder that afflicts more than 50 million people worldwide. Many epilepsy patients can control their symptoms through medication, but about 30% suffer from intractable epilepsy and are unable to manage the disease with drugs. Intractable epilepsy causes multiple seizures, permanent mental, physical, and developmental disabilities, and even death. Therefore, surgical removal of the affected area from the brain has been used as a treatment for patients with medically refractory seizures, but this too fails to provide a complete solution because only 60% of the patients who undergo surgery are rendered free of seizures.
A Korean research team led by Professor Jeong Ho Lee of the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and Professor Dong-Seok Kim of the Epilepsy Research Center at Yonsei University College of Medicine has recently identified brain somatic mutations in the gene of mechanistic target of rapamycin (MTOR) as the cause of focal cortical dysplasia type II (FCDII), one of the most important and common inducers to intractable epilepsy, particularly in children. They propose a targeted therapy to lessen epileptic seizures by suppressing the activation of mTOR kinase, a signaling protein in the brain. Their research results were published online in Nature Medicine on March 23, 2015.
FCDII contributes to abnormal developments of the cerebral cortex, ranging from cortical disruption to severe forms of cortical dyslamination, balloon cells, and dysplastic neurons. The research team studied 77 FCDII patients with intractable epilepsy who had received surgery to remove the affected regions from the brain. The researchers used various deep sequencing technologies to conduct comparative DNA analysis of the samples obtained from the patients' saliva or brain and blood. They reported that about 16% of the studied patients had somatic mutations in their brain. Such mutations, however, did not take place in their blood or saliva DNA.
Professor Jeong Ho Lee of KAIST said, "This is an important finding. Unlike our previous belief that genetic mutations causing intractable epilepsy exist anywhere in the human body including the blood, specific gene mutations incurred only in the brain can lead to intractable epilepsy. From our animal model, we could see how a small fraction of mutations carrying neurons in the brain could affect its entire function."
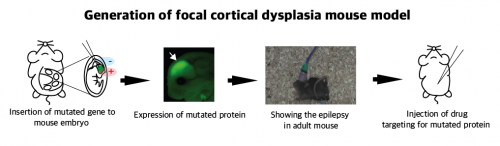
A schematic image shows how to generate a focal cortical dysplasia mouse model. This mouse model opens a new window of drug screening for seizure patients. Credit: KAIST
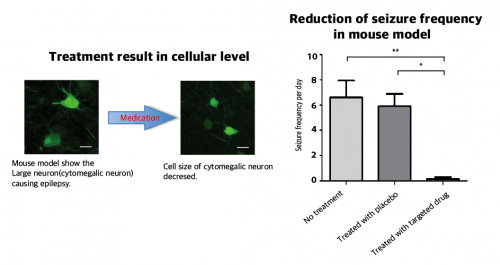
The research team recapitulated the pathogenesis of intractable epilepsy by inducing the focal cortical expression of mutated mTOR in the mouse brain via an electroporation method and observed as the mouse developed epileptic symptoms. They then treated these mice with a drug called "rapamycin" to inhibit the activity of mTOR protein and observed that it suppressed the development of epileptic seizures with cytomegalic neurons.
Targeted medicine can rescue focal cortical dysplasia symptoms including cytomegalic neuron & intractable epilepsy. Credit: KAIST
"Our study offers the first evidence that brain-somatic-activating mutations in MTOR cause FCDII, and we identified mTOR as a treatment target for intractable epilepsy," said co-author Dr. Dong-Seok Kim, a neurosurgeon at Yonsei Medical Center with the most surgical experiences in treating patients with this condition.
More information: "Brain somatic mutations in MTOR cause focal cortical dysplasia type II leading to intractable epilepsy." DOI: 10.1038/nm.3824
Journal information: Nature Medicine