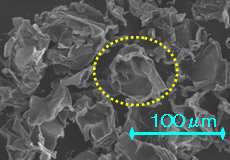
Petaloid μ-piece: “Petaloid” means “resembling a flower petal”. A petaloid μ-piece has a detailed structure with complex surfaces.
Fujifilm Corporation has developed the micro-sized petaloid µ-pieces of Recombinant Peptide (RCP), a scaffold material required for cell cultivation and transplantation in regenerative medicine. It has been verified that the "CellSaic (Cell and Scaffold, forming Mosaic)," which is a three-dimensional mosaic cell structure that consists of RCP petaloid µ-pieces and cells, substantially increases the cells' survival rate in mice transplantation compared to cell-only transplantation. In the study using Type I diabetic model mice, the co-transplantation of CellSaic, which combines RCP petaloid µ-pieces with the human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSC) and the cells from pancreatic islet, which controls blood glucose level, successfully lowered the blood glucose level to a normal level.
When cells are cultured with RCP petaloid µ-pieces in a culture plate, after five days, double the number of cells survived compared to the culturing of cells alone.
The research results will dramatically improve the efficiency of cell transplantation to enable the regeneration of tissues and organs. They represent an epoch-making research outcome that makes a significant contribution to the advancement of regenerative medicine.
Regenerative medicine is a new medical technology that involves regenerating damaged organs and tissues and restores their functionality. Cell transplantation and tissue transplantation, in particular, are considered to be the technologies of greatest potential. In order to make transplanted cells and tissues function properly, it is important to (1) effectively achieve in vivo survival of the transplanted cells and tissues, and (2) enable the supply of nutrients / oxygen to and discharge of waste products from the transplanted tissues and cells. The use of a material that serves as cellular scaffold is generally considered as an effective approach for in vivo survival of transplanted cells and tissues, while the early introduction of blood vessels is considered to be an effective way of facilitating the supply of nutrients / oxygen as well as the discharge of waste products. However, the larger a spheroid the difficult it becomes to supply nutrients / oxygen into its core and facilitate the discharge of waste products. Cells end up dying before a blood vessel can be established.
To counter this problem, Fujifilm used advanced engineering technology to process its proprietary scaffold material "RCP", which does not contain any animal-derived ingredient, to newly develop its micro-sized petaloid μ-pieces. These were combined with cells to create a three-dimensional mosaic cell structure called "CellSaic", which has been used to produce the following research outcomes:
Verifying that the CellSaic substantially raises the survival rate of cells transplanted in vivo
1. Experiment description
In order to facilitate the supply of nutrients / oxygen and discharge of waste products, the study made subcutaneous transplantation of CellSaic, which combines hMSC with petaloid µ-pieces optimally shaped for cellular survival, into mice's back, and compared the rate of cellular survival against the transplantation of only hMSC spheroids.
2. Results
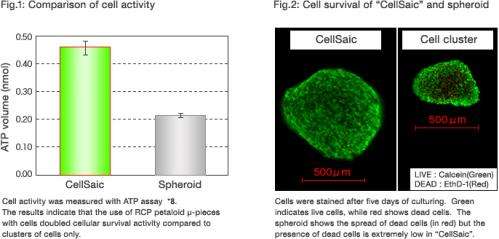
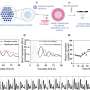
Combining hMSC with RCP petaloid µ-pieces into "CellSaic" more than doubled the survival activity of cells after seven days of cultivating compared to spheroids of hMSC alone (Fig.1).
It was visually confirmed that, despite the growth of the "CellSaic", the number of dead cells was very small inside the "CellSaic", suggesting the survival of numerous cells (Fig.2).
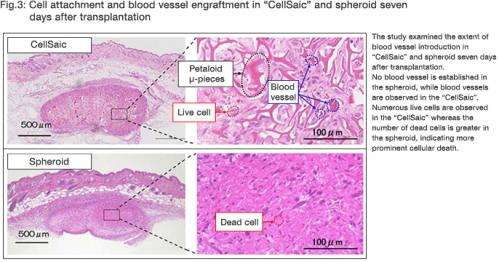
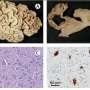
Seven days after transplantation, compared to hMSC spheroids, CellSaic showed a significantly more prominent introduction of blood vessels, which are passageways of nutrients, oxygen and waste products. At the same time, it was also confirmed that cellular survival was substantially higher in CellSaic (Fig.3).
These results indicate:
"RCP" in petaloid μ-pieces secured cell scaffold, and created space inside "CellSaic" at the same time, facilitating the supply of nutrients / oxygen and discharge of waste products.
"RCP" and the extra "space" provided channels for in-vivo vascular cells to arrive.
Successfully lowering the blood glucose level in pancreatic islet transplantation in Type I diabetic model mice
1. Experiment description:
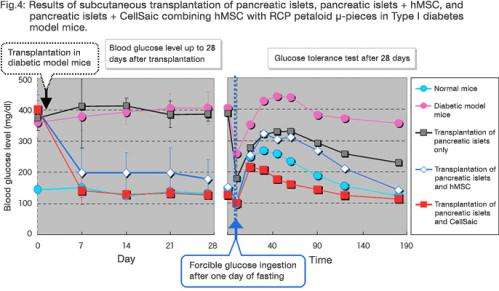
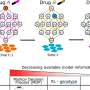
Pancreatic islet transplantation is an advanced medical treatment available for pancreatic islet dysfunction such as Type I diabetes, which causes difficulty in control of the blood glucose level. Animal tests have reported enhanced treatment outcome of pancreatic islet transplantation, when mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) are co-transplanted. This study prepared "CellSaic" combining hMSC with petaloid µ-pieces, and co-transplanted the CellSaic and pancreatic islets into the Type I diabetic model mice.
2. Results
The subcutaneous co-transplantation of pancreatic islets and CellSaic, combining hMSC with RCP petaloid µ-pieces, into mice produced a higher treatment effect than the co-transplantation of pancreatic islets and hMSC, and successfully lowered blood glucose to the normal level (Fig.4).
Compared to the conventional approach, this co-transplantation led to the greater in vivo survival of hMSC cells, indicating enhancement of the effect of pancreatic islet transplantation.
Fujifilm will continue to integrate its expertise in highly-functional materials and engineering technologies, fostered over many years of research in photographic films, with technologies and know-how of its affiliate, Japan Tissue Engineering Co., Ltd., in research, development, production and marketing to further promote R&D in regenerative medicine and contribute to its future industrialization.
Provided by Fujifilm