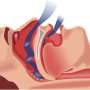
(HealthDay)—Obesity is associated with increased odds of respiratory events and more frequent need for airway intervention in patients undergoing pediatric procedural sedation, according to a study published online March 27 in Pediatric Anesthesia.
Patricia D. Scherrer, M.D., from Children's Hospitals and Clinics of Minnesota in Minneapolis, and colleagues queried the Pediatric Sedation Research Consortium database to compare sedation-related outcomes, adverse events, and therapeutic interventions for obese and nonobese patients. Of the 28,792 records that were eligible, 5,153 patients were obese.
The researchers found that total adverse events were more frequent in obese patients (odds ratio [OR], 1.49). Obese patients had increased respiratory events (airway obstruction: OR, 1.94; oxygen desaturation: OR, 1.99; secretions: OR, 1.48; and laryngospasm: OR, 2.30), inability to complete the associated procedure (OR, 1.96), and prolonged recovery (OR, 2.66). Airway interventions, including repositioning, suctioning, jaw thrust, airway adjuncts, and bag-valve-mask ventilation, were more frequently required in obese patients. In multivariate analysis, obesity was independently associated with minor and moderate, but not major, adverse events.
"Obesity is an independent risk factor for adverse respiratory events during procedural sedation and is associated with an increased frequency of airway interventions, suggesting that additional vigilance and expertise are required when sedating these patients," the authors write.
More information:
Abstract
Full Text (subscription or payment may be required)
Copyright © 2015 HealthDay. All rights reserved.