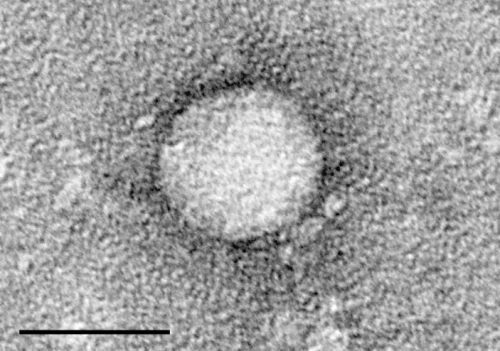
Electron micrographs of hepatitis C virus purified from cell culture. Scale bar is 50 nanometers. Credit: Center for the Study of Hepatitis C, The Rockefeller University.
Treatment options for chronic hepatitis C, a serious and life-threatening infection, have improved substantially and several new regimens with shorter durations and improved efficacy and safety profiles are now available.
Groups have raised concerns about the evidence used to support the approval of some newer drugs, however, and the issue has been used to cast doubt on their efficacy and even to question treatment or deny reimbursement.
To address these concerns, the US Food and Drug Administration's Division of Antiviral Products in the Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) has published a paper that highlights the agency's scientific approaches and regulatory processes that support the development and approval of promising drugs to treat hepatitis C.
"FDA's approach to evaluation of recent hepatitis C drugs underscores the Agency's flexibility in considering innovative or alternative trial designs for drugs that have demonstrated highly promising outcomes in early phase development," said Dr. Poonam Mishra, deputy director for Safety, Division of Antiviral Products/Office of Antimicrobial Products in the FDA's Center for Drug Evaluation and Research and lead author of the Hepatology paper. "Expedited approaches can be used without compromising efficacy standards for drugs that demonstrate breakthrough therapy potential."
Provided by Wiley