Human visual cortex holds neurons that selectively respond to intermediate colors
Researchers from Tohoku University's Research Institute of Electrical Communication and RIKEN BSI have found the presence of neurons in the human brain which can each selectively respond to an intermediate color; not just neurons of red, green, yellow and blue.
It was previously believed that the human visual system encoded color information through combinations of four opponent colors - red/green, yellow/blue - and dark/light components. In this format, orange can be represented as the combination of red and yellow, and purple as a combination of blue and red.
However, recent electrophysiological studies in primates have revealed the presence of neurons in the visual cortex, each of which are selective to intermediate color.
Studies using human participants - through psychophysical and brain-activity-imaging techniques - have also shown indirect evidence of the presence of those neurons, although no direct recording of hue-selective response has yet been made, and the variability and population of neurons selective to intermediate colors have not been reported explicitly in humans.
The research group succeeded in recording neuronal responses selective to intermediate hues in human brains by using a functional MRI technique.
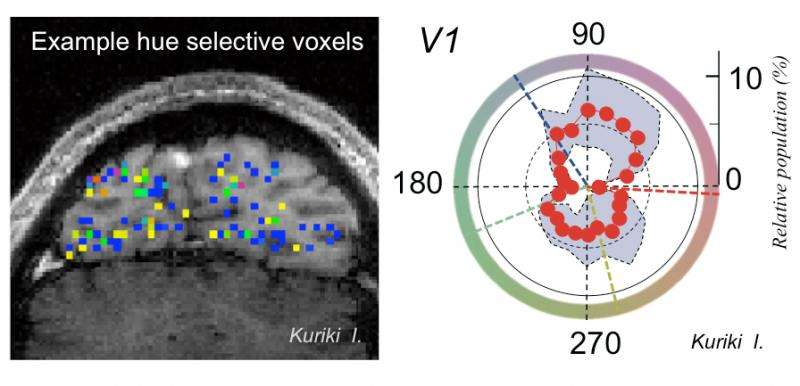
During the measurement of brain activity, subjects were shown a circular checkered pattern which gradually changed its color along a hue circle (Figure: right panel, outer ring). The study was done under an equal light intensity carefully adjusted beforehand in each subject.
The time course of brain activity was analyzed for each pixel (voxel) of the fMRI data (Figure : left panel). For example, if the response of a voxel was dominated by neurons selective to a particular hue, it would exhibit a maximum response when the selective hue is presented.
The results were summarized, in terms of the voxel count selective to each hue direction, as histograms. An example of averaged histograms for the primary visual cortex (V1: one of four brain regions measured in the study) is shown in the figure (right panel). The study's results also confirmed that the cortical responses selective to intermediate hues are not just the combined responses of the four opponent hues.
This is the first report in the world, of the histogram of neurons selective to each hue, including intermediate hues, in human subjects. Full findings of the study will appear in the British scientific journal Cerebral Cortex as an open-access article on September 30.
The researchers believe the result of the study may provide clues to the design of multi-primary-color displays. Usual displays have 3 color primaries (usually red, green, and blue), but color-rendering precision becomes higher when 6 color primaries are employed. Such displays have been studied for the presentation of high-quality/precision/fidelity color images that can be used, for example, for medical or clinical purpose.
Since the histogram (Figure: right panel) infers that people are possibly more sensitive to hues of larger population, it may be possible that displays with primary colors chosen among the larger population hues would be able to render more precise colors with a higher efficacy to the human brain.