Development of low cost oral inactivated vaccines for dysentery

Okayama University researchers, in collaboration with colleagues in India, have developed inactivated vaccines, a promising candidate for the production and commercialization of a low-cost oral dysentery vaccine for use in developing countries.
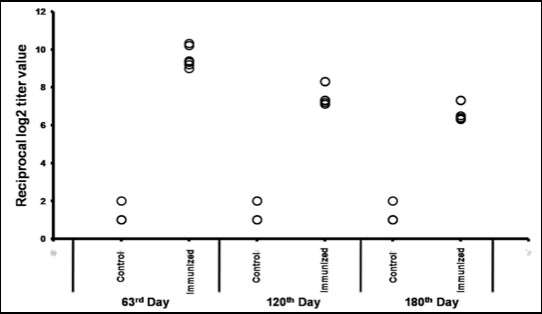
Shin-ichi Miyoshi at the Okayama University Graduate School of Medicine and Dentistry and colleagues orally administered a mixture of the six major Shigella serotypes of heat-killed bacteria sample preparations to laboratory animals in order to explore the possibility of inactivated vaccines. The researchers conducted experiments using both passive and active immunization experimental systems and observed protective effects against infections with sufficient immunity-inducing effect.
Furthermore, in tests using human cultured cells, the researchers found no cell toxicity and observed strong production inducing immunity factors such as cytokines. This sample preparation is a promising candidate for an orally administered dysentery vaccine. In the future, using the rhesus monkeys, which are natural hosts of shigella, the researchers plan to study the protective and immunity-inducing effects.
Background and expected outcome
In 2007, the university established the Okayama University India Infection Joint Research Centre to contribute to the control of the many deaths due to diarrhea in India. One of the research projects concerns the development of an inexpensive oral dysentery vaccine, due to the lack of dysentery vaccines for practical use.
Dysentery destroys intestinal tissue, causing severe bleeding with deaths in developing countries such as India, affecting 600,000 people annually. For this reason, the World Health Organization has designated the development of dysentery vaccine to be one of the most urgent research areas. Today, drug-resistant shigella is spreading fast and its treatment and the control of dysentery is becoming increasingly difficult.
The results of this research are expected to lead to the development and commercialization of low-cost dysentery vaccines before the control of dysentery becomes extremely difficult.
More information: Soumik Barman et al. Passive immunity with multi-serotype heat-killed Shigellae in neonatal mice, Microbiology and Immunology (2014). DOI: 10.1111/1348-0421.12164
Dhrubajyoti Nag et al. Heat killed multi-serotype Shigella immunogens induced humoral immunity and protection against heterologous challenge in rabbit model, Immunobiology (2015). DOI: 10.1016/j.imbio.2015.07.002