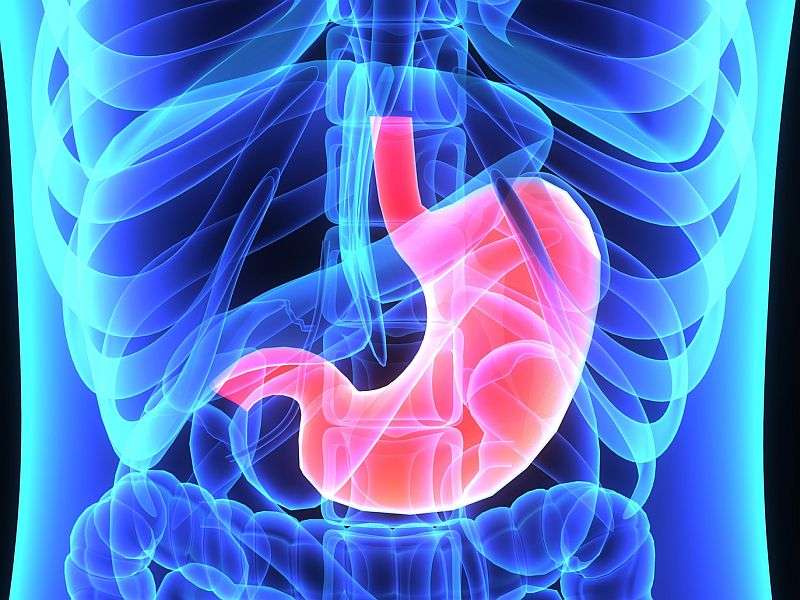
(HealthDay)—Recommendations have been updated for treatment of Helicobacter pylori in adults, according to a consensus statement published in the July issue of Gastroenterology.
Carlo A. Fallone, M.D., from the McGill University Health Centre in Montreal, and colleagues conducted a systematic literature review and developed specific, updated recommendations for eradication therapy in adults with H. pylori infection.
The researchers strongly recommend that all H. pylori regimens should be given for 14 days because of the increasing failure of therapy. Concomitant nonbismuth quadruple therapy (proton pump inhibitor [PPI] + amoxicillin + metronidazole + clarithromycin [PAMC]) and traditional bismuth quadruple therapy (PPI + bismuth + metronidazole + tetracycline [PBMT]) were included as recommended first-line strategies. Use of PPI triple therapy (PPI + clarithromycin + amoxicillin or metronidazole) should be limited to regions with low resistance to clarithromycin or high eradication success with these regimens. PBMT and levofloxacin-containing therapy were included as recommended rescue therapies. Rifabutin therapy should be used only for patients who have failed to respond to three or more previous treatment regimens.
"Optimal treatment of H. pylori infection requires careful attention to local antibiotic resistance and eradication patterns," the authors write. "The quadruple therapies PAMC or PBMT should play a more prominent role in eradication of H. pylori infection, and all treatments should be given for 14 days."
Several authors disclosed financial ties to the pharmaceutical industry.
More information:
Abstract
Full Text (subscription or payment may be required)
Journal information: Gastroenterology
Copyright © 2016 HealthDay. All rights reserved.