MRI scans for suspected prostate cancer could improve diagnosis
A researcher from Hull York Medical School (HYMS) has helped design and set up a study which has been hailed as the biggest leap in diagnosing prostate cancer in decades.
The study, published in The Lancet medical journal, was led by researchers from University College London, with collaboration from a multi-disciplinary team including Dr Rhian Gabe from HYMS.
Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in British men. If men have high prostate specific antigen (PSA) levels in the blood, they are referred for a biopsy.
Researchers revealed that an advanced MRI technique can pick up 93 per cent of aggressive cancers, compared with 48 per cent for a standard biopsy.
The study on 576 men showed more than a quarter could be spared invasive biopsies
The current standard technique for prostate biopsy can miss a cancer that is there, fail to spot whether it is aggressive, and biopsies can cause side-effects including bleeding, serious infections and erectile dysfunction.
Around 100,000 to 120,000 men go through this every year in the UK.
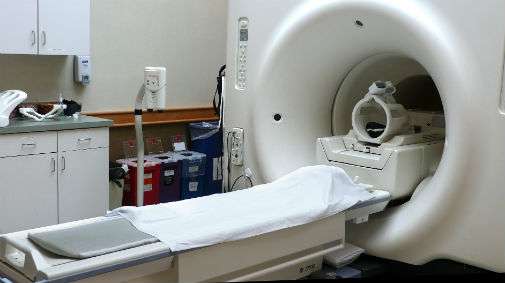
The trial, at 11 hospitals in the UK, used multi-parametric MRI on men with high PSA levels.
Dr Gabe said: "The study is ground-breaking because of the implications for future recommendations regarding diagnostic tests for prostate cancer and the potential benefit derived by the vast numbers of men referred for prostate biopsies on the basis of elevated PSA levels.
"The study has highlighted inadequacies with standard biopsies with only half the clinically significant cancers being detected in a cohort of men with elevated PSA.
"The results also suggest that advanced MRI prior to biopsy could identify about a quarter of men who could safely avoid unnecessary biopsies and in future, could be used to guide prostate biopsy to greatly improve detection of clinically significant cancer."
For this strategy to be implemented across the NHS, a number of important capacity issues such as training of radiologists would be need to be addressed, Dr Gabe added.
More information: Hashim U Ahmed et al. Diagnostic accuracy of multi-parametric MRI and TRUS biopsy in prostate cancer (PROMIS): a paired validating confirmatory study, The Lancet (2017). DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)32401-1