Credit: University College London
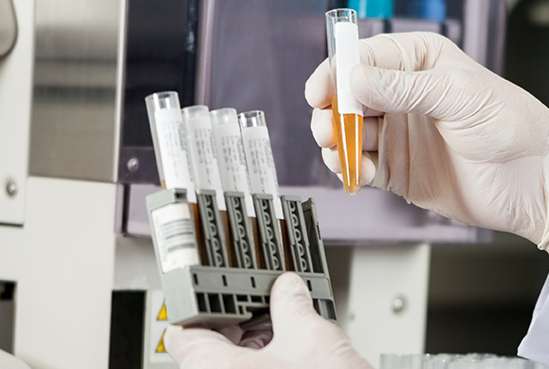
A new test for bladder cancer could enable GPs to test a urine sample and spare patients the discomfort of a cystoscopy in hospital, according to UCL research published today in Clinical Epigenetics.
The test, called UroMark, has been developed by UCL researchers and uses cutting edge genomic sequencing to detect abnormal cancer DNA in a urine sample. The research team, led by Professor John Kelly and Dr Andy Feber (UCL Cancer Institute), identified a panel of DNA alterations which are highly specific to bladder cancer and found that when used on DNA from urine, UroMark detected bladder cancer with a high degree of accuracy (98% of cases), equivalent to a cystoscopy, currently the clinical gold standard.
The study was carried out on 300 patients and the UK Medical Research Council has awarded £1.42 million for two larger trials which are currently underway across 32 hospitals. The trials will confirm the accuracy of UroMark before it becomes widely available for clinical use.
Approximately 11,000 people are diagnosed with bladder cancer each year in the UK. For most people, an early sign of bladder cancer is blood in their urine (haematuria), but many patients experience symptoms such as recurrent infection; and the urgency and irritation to urinate.
Normally, patients with blood in their urine are sent to hospital for tests, which include passing an instrument along the water pipe or urethra to inspect the bladder (cystoscopy). The new test will avoid the need for cystoscopy for many patients and can be tested by GPs if cancer is suspected.
Professor John Kelly said: "We have good evidence that patients, particularly females, are diagnosed late with bladder cancer and often patients visit a GP several times with symptoms prior to detection. Having the UroMark test available to GPs will mean that patients can be tested at an early stage to rule out bladder cancer."
The team anticipate that UroMark will reduce the costs of having to refer patients to hospital. In the UK around 110,000 cystoscopies are performed each year, at a cost to the NHS in the region of £55.39 million.
More information: Andrew Feber et al. UroMark—a urinary biomarker assay for the detection of bladder cancer, Clinical Epigenetics (2017). DOI: 10.1186/s13148-016-0303-5
Provided by University College London