How parenting styles influence our attitudes to marriage
Research from Japan has revealed how different parenting styles can affect marriage rates and desired number of children.
This research was led by Project Professor NISHIMURA Kazuo (Kobe University) and Professor YAGI Tadashi (Doshisha University). It was carried out as part of the RIETI project "Fundamental Research for Sustainable Economic Growth in Japan", using data from an online survey of 10,000 people carried out in January 2016 through Rakuten Research, Inc. The study identifies archetypal parenting methods in Japan and their influence on children's lives.
Parenting methods were categorized as supportive, strict (tiger), indulgent, uninvolved, and abusive. For both men and women, the supportive approach to parenting produced the highest achievements in income, happiness levels, and academic achievement for children.
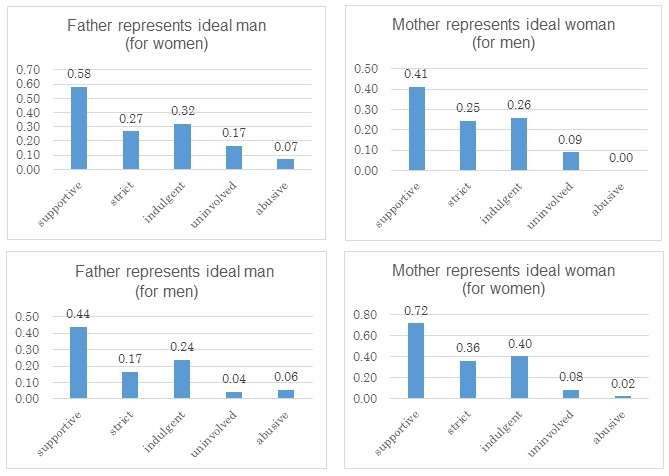
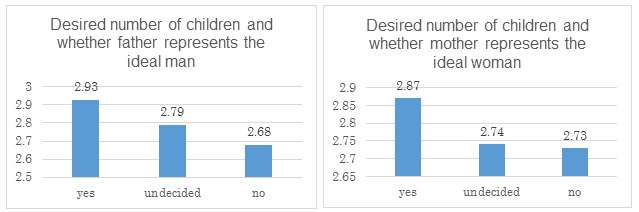
The team also analyzed the effects of different parenting styles on respondents' attitudes towards their mothers and fathers, and how enthusiastic they are about starting families of their own. They discovered that people who had received a supportive upbringing were most likely to see their own father or mother as the ideal, whereas respondents who had experienced abusive parenting styles were least likely to view their own parents as positive models for themselves or potential partners. Marriage rates are higher among people whose ideal partner or self is represented by their own father or mother, and this group also wanted more children.
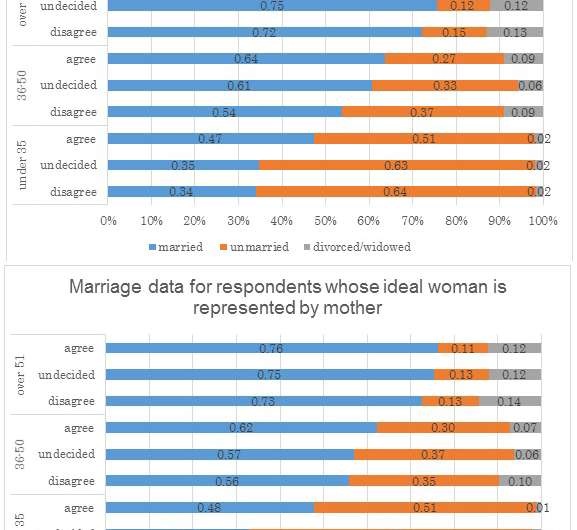
"People with a supportive upbringing are more likely to see their parents as positive role models", said Professor Nishimura. "Our findings show that this attitude is also linked to higher marriage rates, and a desire for larger numbers of children."
Types of parenting
- Supportive:
High or average levels of independence, high levels of trust, high levels of interest shown in child, large amount of time spent together - Strict (tiger):
Low levels of independence, medium-to-high levels of trust, strict or fairly strict, medium-to-high levels of interest shown in child, large amount of rules - Indulgent:
High or average levels of trust, not strict at all, time spent together is average or longer than average - Uninvolved:
Low levels of interest shown in child, not strict at all, small amount of time spent together, few rules - Abusive:
Low levels of interest shown in child, low levels of independence, low levels of trust, strict