How a disease outbreak affects a group of animals depends on the breakdown of ages in the population, an animal study has shown. The findings could help scientists better understand how events such as disease outbreaks may affect certain groups in a population.
Scientists sought to examine how a spread of ages can influence a population's health, by simulating an outbreak of disease in small marine animals.
Age dependency
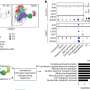
With lab experiments and computer modelling, they found that disease spread can vary depending on the age at which individuals are exposed to infection, and the age at which females in the group become mothers. Experiments in the latest study found that offspring of younger mothers were more at risk from infection. The finding builds upon previous knowledge that younger individuals are more at risk.
Taking these factors into account, computer models showed that when death rates are high, disease can spread faster – even as populations fall. This contradicts the expectation that disease should spread most easily in dense populations, in which individuals interact more.
Modelling response
Researchers from the University of Edinburgh carried out lab experiments with water fleas, examining how four generations of the small crustaceans responded to a common bacterial infection. Their results were used to build a mathematical model of how the organisms might respond in the long term to threats such as incidence of disease.
Their study is published in Ecology Letters.
Provided by University of Edinburgh