Mouse study helps find genetic causes of human behavioral disorders
Scientists studying the role of a protein complex in the normal development of the mouse brain unexpectedly created a mouse model that replicates clinical symptoms of patients with complex neurological disorders such as hyperactivity, learning deficits and social behavior abnormalities. Careful study of this mouse model led to the discovery of the genetic cause of the human neurological condition of five patients who, until now, had not received a genetic diagnosis. The team, which includes researchers, from Baylor College of Medicine, Texas Children's Hospital and other institutions, has published the results in Nature Genetics.
"When we began this research, we were just curious about what the ATXN1-CIC complex normally does," said senior author Dr. Huda Zoghbi, professor of molecular and human genetics and of pediatrics - neurology and developmental neuroscience at Baylor and director of the Jan and Dan Duncan Neurological Research Institute at Texas Children's Hospital.
The researchers knew that enhanced function of the ATXN1-CIC complex can lead to neurodegenerative conditions. In this work, to discern the role of the complex in the development of a normal brain, they explored the biological consequences of the opposite situation, the complex losing its function. Using genetic tools in the lab, the researchers selectively removed genes involved in the formation of the complex in distinct regions of the mouse brain; the forebrain, and the hypothalamus and amygdala.
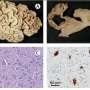
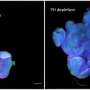
"We discovered that genetically removing the complex from forebrain cells resulted in learning and memory deficits and hyperactivity in the mice," said co-first author Dr. Qiumin Tan, postdoctoral fellow of molecular and human genetics in the Zoghbi lab. "Interestingly, within the forebrain, only the upper layers of the cortex showed a reduction of thickness, while lower layers appeared intact."
"The biggest surprise was how the fairly specific and relatively limited changes in the cortex caused dramatic hyperactivity in mice," said co-first author Dr. Hsiang-Chih Lu, who was a doctoral student in the Zoghbi lab during this study and is currently at Washington University.
When the researchers knocked out genes involved in the protein complex only in the hypothalamus and amygdala, they observed changes in the mice behavior that were different from those described above. "In this case, the mice showed prominent deficits in their social interactions," Tan said. "For instance, they interacted less with other mice, and spent less time interacting with unfamiliar mice. These behaviors resemble some of the behaviors observed in individuals with autism spectrum disorders."
In contrast to the marked changes in thickness observed in the cortex, the researchers did not observe any major alterations in the structure of hypothalamus and amygdala when they lacked the protein complex.
Intrigued by their findings in mice, the researchers decided to investigate whether similar genetic changes in humans would be associated with comparable behaviors.
"If we hadn't seen these neurological problems in the mice, we would not have looked for the human parallel," Zoghbi said.
The human connection
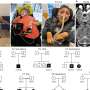
To find individuals carrying mutations in the genes involved in the formation of the ATXN1-CIC complex, the researchers entered the candidate genes they had worked with in mice in GeneMatcher, a web-tool developed as part of the Baylor-Hopkins Center for Mendelian Genomics for rare disease researchers. Similar to online dating websites that match couples, GeneMatcher allows researchers to find others that are interested in the same genes they are working on.
"Through GeneMatcher we found five individuals carrying a mutation in capicua, one of the genes linked to the ATXN1-CIC complex," Tan said. "Taken together, the affected individuals present with a spectrum of behavioral disorders including attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), developmental delay and intellectual disabilities and some have autism and epileptic seizures."
These individuals did not have an explanation for their condition; they did not know it was a genetic disorder or what had caused it. This work has provided them with an answer; researchers can now better understand the biology of their hyperactivity and intellectual disability.
"Hyperactivity is a relatively common problem in children, but it's been hard to understand it biologically," Zoghbi said. "I think our work has pointed out an area of the brain in which we can begin to investigate to understand what drives this behavior."
"Some people have suggested that mouse models are not good enough to study human diseases. I think that the models are good, what is important is how we study them," Zoghbi said. "In this case, careful study of the mouse models has shown us where to look in human patients to potentially find the biological underpinnings of complex behavioral disorders, such as ADHD and autism spectrum disorder."
"This work has shown that the ATXN1-CIC complex is important for proper development and function of the brain and also uncovers its roles in human neurodevelopmental disorders," Lu said.
More information: Hsiang-Chih Lu et al. Disruption of the ATXN1–CIC complex causes a spectrum of neurobehavioral phenotypes in mice and humans, Nature Genetics (2017). DOI: 10.1038/ng.3808