Visceral fat differentiates crohn's from intestinal tuberculosis
(HealthDay)—Visceral fat (VF) quantification can differentiate Crohn's disease (CD) and intestinal tuberculosis (ITB), according to a study published in the February issue of the Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
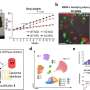
Dawesh Prakash Yadav, M.B.B.S., M.D., from the All India Institute of Medical Sciences in New Delhi, and colleagues examined the role of VF in differentiating CD and ITB in two cohorts (development and validation). Retrospective data were collected for 75 patients with CD and ITB in the development cohort. In the validation cohort, 82 patients were recruited prospectively and were diagnosed as CD or ITB according to standard diagnostic criteria.
The researchers found that visceral fat area and the VF/subcutaneous (SC) fat ratio were significantly higher in CD than ITB patients in both the cohorts (development: 106.2 ± 63.5 versus 37.3 ± 22 [P < 0.001] and 1.1 ± 0.57 versus 0.43 ± 0.24 [P = 0.001], respectively; validation: 102.2 ± 69.8 versus 55.8 ± 44.9 [P = 0.01] and 1.2 ± 0.68 versus 0.56 ± 0.33 [P < 0.001], respectively). In the development cohort, a cut-off of 0.63 for VF/SC ratio had high sensitivity and specificity for differentiating CD and ITB (82 and 81 percent, respectively). When this cut-off was applied in the validation cohort, the sensitivity and specificity were similar (81 and 79 percent, respectively).
"The VF/SC ratio is a simple, cost-effective, non-invasive, and single objective parameter with a good sensitivity and specificity to differentiate CD and ITB," the authors write.
More information:
Abstract
Full Text (subscription or payment may be required)
Copyright © 2017 HealthDay. All rights reserved.