Surveillance biopsy timing not tied to reclassification

(HealthDay)—Timing of the first active surveillance biopsy is not associated with increased adverse reclassification of prostate cancer, according to a study published in the April issue of The Journal of Urology.
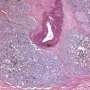
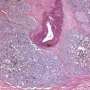
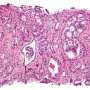
Liam C. Macleod, M.D., from the University of Washington in Seattle, and colleagues analyzed the Canary PASS (Prostate Cancer Active Surveillance Study) to determine biopsy timing influence on rates of prostate cancer adverse reclassification at the first active surveillance biopsy. An increase in Gleason sum and/or 34 percent or more of cores with prostate cancer were used to define reclassification.
The researchers found that 21.1 percent of 421 men experienced reclassification at the first active surveillance biopsy. Eleven months was the median time from prostate cancer diagnosis to first active surveillance biopsy. Reclassification rates were 24 percent at <8 months, 19 percent at 8 to 13 months, and 22 percent ≥13 months (p = 0.65). The odds ratio (OR) of reclassification at 8 to 13 months and ≥13 months was 0.88 (95 percent confidence interval, 0.5 to 1.6) and 0.95 (95 percent confidence interval, 0.5 to 1.9), respectively, versus men biopsied at <8 months. Increased odds of reclassification were seen with prostate-specific antigen density ≥0.15 (referent <0.15; OR, 1.9) and body mass index ≥35 kg/m² (referent <25 kg/m²; OR, 2.4) were associated with increased odds of reclassification.
"In low risk patients on active surveillance, it may be reasonable to perform the first active surveillance biopsy at a later time, reducing the overall cost and morbidity of active surveillance," the authors write.
More information:
Abstract
Full Text
Copyright © 2017 HealthDay. All rights reserved.