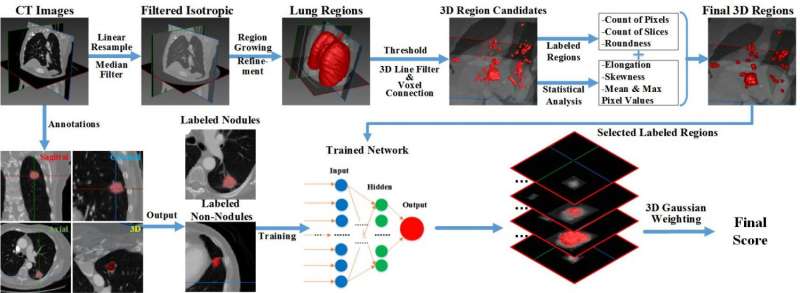
The pipeline of the proposed nodule detection method. Credit: ©Science China Press
Lung cancer is among the most deadly cancers. In contrast to the steady increase in survival for most cancers, advances have been slow for lung cancer. Typically, the five-year survival rate for lung cancer patients is 16 percent, which rises to 52 percent if lung cancer is diagnosed at early stages. However, it decreases to below 4 percent if metastasis occurs. Therefore, it is of crucial importance to detect lung cancer at early stages in order to prolong the patient's life. Liu et al. from Beihang University have proposed an artificial neural network system for lung cancer detection, set to be published in the seventh issue of Science China Information Sciences in 2017.
In clinical practice, computer tomography (CT) can capture fine-grained details for both lung nodules and surround structures, comprising the golden standard for diagnosis. However, the high sensitivity of CT imaging also leads to huge data and complex ambiguities, which makes it hard for radiologists to distinguish pathological structures from healthy tissue. In recent years, computer aided detection (CADe) systems have developed rapidly and show great potential in diagnostic assistance. Detection for lung nodules is an obvious application. However, it is hard to assess lung nodules due to variables like nodule appearance, minor differences between nodules and healthy structures, as well as the influence of vessels and other tissues around nodules.
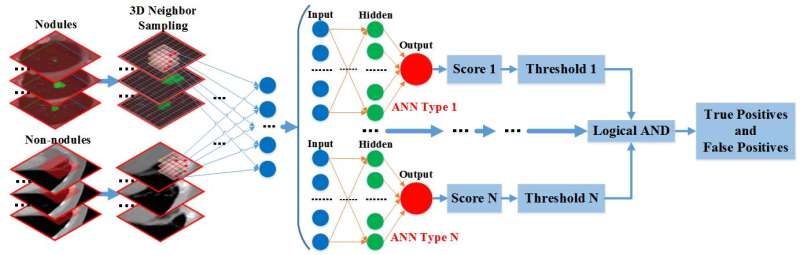
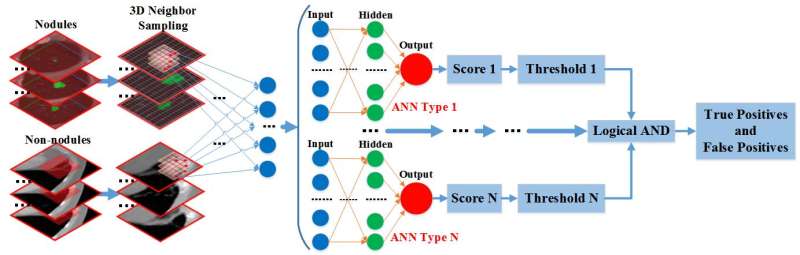
Inspired by prior work, the new article presents an artificial neural network-based approach to the extraction of lung nodules from chest CTs. The pipeline and the ANN architecture can be found in Fig.1 and Fig.2, separately. Different from classical methods, we focus on the inner structures of nodule voxels and apply ANN to generalize these characteristics. We are working in 3-D space consisting of only voxels instead of slice-by-slice processing in CT volume. Our method can be easily integrated into existing CADe systems and rapidly accommodate and process new data streams with few human interactions. Meanwhile, we propose a novel voting method based on geometrical and statistical features to better extract initial candidate regions while suppressing ambiguous structures. Finally, we have proposed a nodule detection approach with multiple trained ANNs based on 3-D massive sampling of candidate voxels instead of user-specified features with a goal to reduce various false positives.
-
ANN network architecture. Credit: ©Science China Press
-
ANN network architecture. Credit: ©Science China Press
More information: Xinglong Liu et al, A CADe system for nodule detection in thoracic CT images based on artificial neural network, Science China Information Sciences (2017). DOI: 10.1007/s11432-016-9008-0
Provided by Science China Press