Link between income inequality and physical activity for women, but not for men
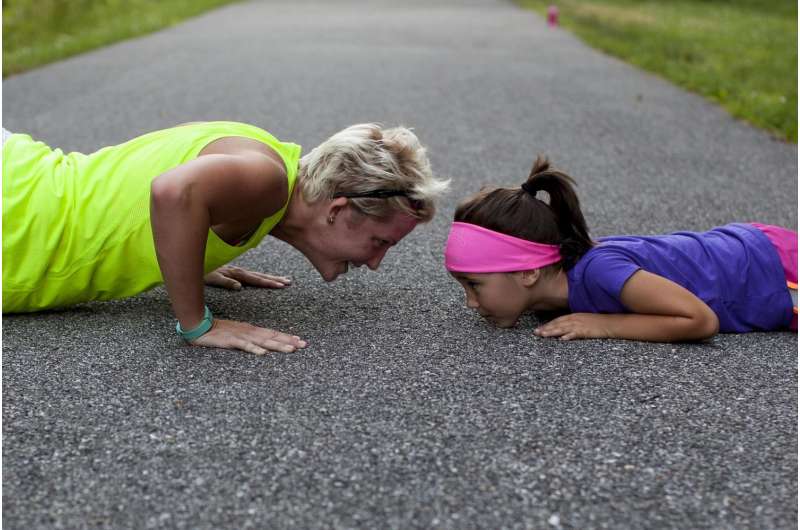

A recent paper published in the Journal of Public Health finds that women from areas with high income inequality are less likely to meet overall physical activity recommendations than men from the same geographical area.
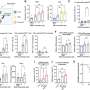
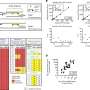
While previous studies have shown that the majority of US adults are not meeting the 2.5 hours of moderate intensity aerobic activity per week recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, this new study is one of the first to investigate the association between state-level income inequality and physical activity for men and women. In analyzing data gathered from over 350,000 adults in the US, the researchers found that, among adult women, high income inequality was associated with a lower likelihood of meeting aerobic, strengthening, and overall physical activity recommendations. The study does not find the same association between state-level income inequality and physical activity for men.
These findings are consistent with other studies which identify how income inequality affects the health of men and women differently and support the suggestion that women's health status might be affected by income equality. However, this paper goes further in drawing an association between the impact of increased income inequality on levels of physical activity and associated health conditions such as obesity and coronary heart disease for women in these areas.
The study suggests that reasons such as increased working hours and greater caring responsibilities for women as well as a growing number of households headed by women are impacting the amount of time available to women for physical activity and therefore increasing the risk of associated conditions.
Despite these findings on women's health, the study does not provide a plausible mechanism for how income inequality relates to coronary heart disease among men. The researchers suggest further investigation to determine why women are less likely to meet physical activity recommendations in states with higher income inequality and to further explore the reasons for the association between income inequality and physical activity.
More information: Roman Pabayo et al, State-level income inequality and meeting physical activity guidelines; differential associations among US men and women, Journal of Public Health (2017). DOI: 10.1093/pubmed/fdx082