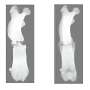
The family relationship between film characters clearly affects the reactions in the viewers' brain
Are we more prone to help the person that resembles us the most? Social neuroscientists have studied the effects of similarity by showing a re-edited version of the film My Sister's Keeper to a group of subjects and by giving them a moral dilemma to consider while measuring their brain function by means of functional magnetic resonance imaging.
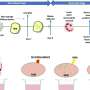
The subjects comprised 30 women who were shown a version of the film shortened to 25 minutes and asked to observe the film in the light of different questions. The study focused particularly on how the subjects felt about one sister refusing to donate an organ to another sister diagnosed with cancer. Before starting the film, the researchers told the subjects that the sisters were either biological siblings or that the younger sister had been adopted to the family as a baby.
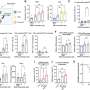
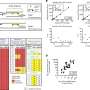
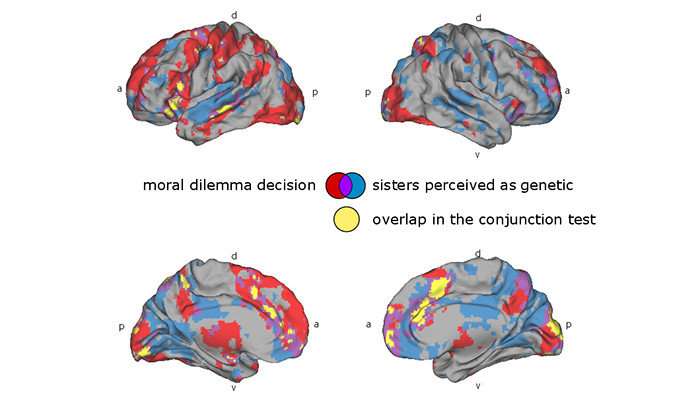
The study discloses a major conflict between what the subjects told they felt about the moral issue presented to them and what actually happened inside their brains. 90 per cent of the subjects responded that genetic relationship between the sisters was of no significance to them compared to a situation in which one of the sisters had been adopted to the family as an infant. Still, functional magnetic resonance imaging reveals major differences in brain function between the two viewing conditions.
"The impact on brain functions was amazingly high when we told about the difference in kinship between the sisters. The brain sees these two situations very differently," says Mareike Bacha-Trams, postdoctoral researcher from Aalto University.
The various impacts of genetic ties
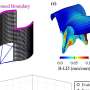
When the viewers thought that the sisters were genetically related there was significant correlation between their brain activity in the insula, cingulate cortex, medial and lateral prefrontal cortex, superior temporal cortex and superior parietal cortex. These areas of the brain control for instance such matters as morals, feelings, and decision-making.
Based on the study, we can thus assume that the moral expectations of the subjects are more similar when the sisters are thought to be genetically related.
The same subjects were also asked to select which one person or several persons they would rather save from a crisis region. A sister, a best friend and unknown people were presented in various combinations, and more than 90 per cent of the subjects said that they would rather save their sister. The best friend came right after the sister. The response times got longer as the subjects had to choose whether they would, in addition to their sister or friend, save four unknown people.
"The study is of significance in the field of social neuroscience when we want to know how people observe interactions between two people with a close relationship. This may also give rise for debate even in situations where scandals related to nepotism emerge in societal decision-making," Professor Iiro Jääskeläinen describes.
More information: Mareike Bacha-Trams et al. Differential inter-subject correlation of brain activity when kinship is a variable in moral dilemma, Scientific Reports (2017). DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-14323-x