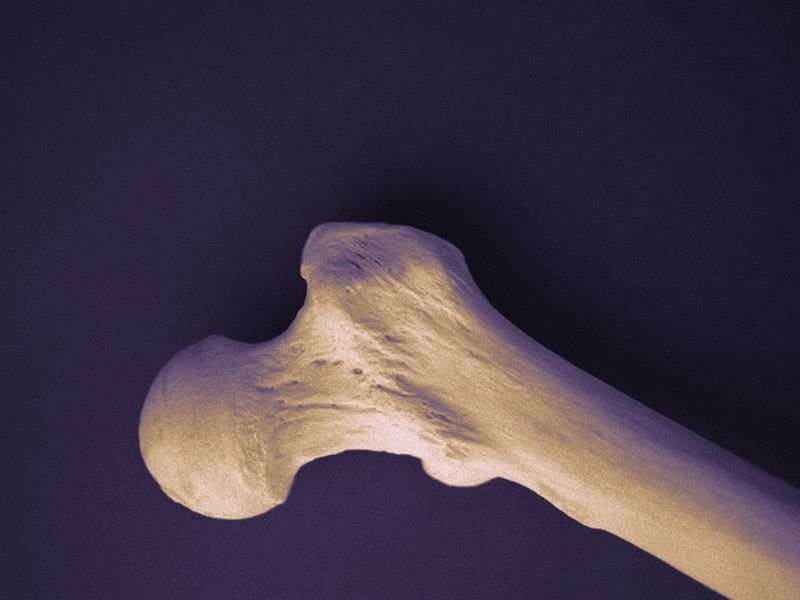
(HealthDay)—Higher dietary total fiber and fruit fiber is protective against bone loss at the femoral neck in men, according to a study published online Oct. 12 in the Journal of Bone and Mineral Research.
Zhaoli Dai, Ph.D., from the Boston University School of Medicine, and colleagues examined the correlation between dietary fiber, assessed using the Willett food frequency questionnaire, and bone loss at the femoral neck, trochanter, and lumbar spine in older men and women. Bone mineral density was measured using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry at baseline (1996 to 2011) and in 2001 to 2005 and 2005 to 2008 among 792 men and 1,065 women.
The researchers found that in men, but not women, higher dietary total fiber and fruit fiber was protective against bone loss at the femoral neck (P = 0.003 and 0.008, respectively). Compared with men in quartile 1 of fiber intake, those in quartiles 2 to 4 had significantly less bone loss at the femoral neck (all P < 0.04). There were no associations with hip bone loss in women; fiber from vegetables seemed protective against spine bone loss in women but not men. No correlations were seen for cereal fiber or nut and legume fiber with bone loss in men or women.
"Our findings suggest that higher dietary fiber may modestly reduce bone loss in men at the hip," the authors write.
More information:
Abstract
Full Text (subscription or payment may be required)
Journal information: Journal of Bone and Mineral Research
Copyright © 2017 HealthDay. All rights reserved.