Magnet-based drug delivery system shows promise for cancer treatment

A team of researchers at the University of Georgia has developed a non-invasive method of delivering drugs directly to cancerous tissue using magnetic forces, a form of treatment that could significantly reduce the toxic side effects of chemotherapy.
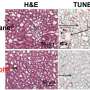
"We showed that we can deliver anti-cancer drugs exactly in the area where they are needed and they can kill cancer cells," said Andrey Zakharchenko, a graduate student in the Nanostructured Materials Lab in the UGA College of Family and Consumer Sciences who led the study.
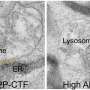
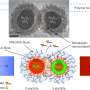
The researchers from UGA and Clarkson University in New York first created very fine nanoparticles that acted as drug carriers, one a substrate base carrying the drugs, and the other loaded with enzymes.
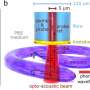
Upon application of a relatively weak magnetic field, the two nanoparticles merge, forcing a reaction that releases the drugs at a specific location.
By controlling the timing of the interaction, researchers could pinpoint delivery of the drug to a precise location, thus preventing side common side effects of chemotherapy, such as hair loss or cardiac toxicity.
Researchers performed the proof of concept study in vitro using chemotherapy drugs and cancer cells. The next step would be to develop an animal model, Zakharchenko said.
The use of a static magnetic field to cause the reaction is important because it poses no threat to the body, said Sergiy Minko, the Georgia Power Professor of Fiber and Polymer Science within the FACS department of textiles, merchandising and interiors and the Franklin College of Arts and Sciences department of chemistry.
In previous studies, pulsating magnetic fields have been used to deliver drugs, but the heat caused by the application can destroy healthy cells of patients.
The article appears in the January issue of the journal Nature Catalysis.
More information: Andrey Zakharchenko et al. Magnetic field remotely controlled selective biocatalysis, Nature Catalysis (2017). DOI: 10.1038/s41929-017-0003-3