No benefit for MRI after normal cervical CT in blunt trauma
(HealthDay)—For patients with obtunded blunt trauma to the cervical spine, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) follow-up appears not to be beneficial after normal cervical computed tomography (CT) findings, according to a study published online March 14 in JAMA Surgery.
Xiao Wu, from the Yale School of Medicine in New Haven, Conn., and colleagues conducted a cost-effectiveness analysis to assess an average patient (aged 40 years) with blunt trauma. The utility and cost-effectiveness of MRI versus no follow-up after normal cervical CT findings were assessed.
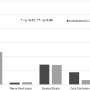
The researchers found that the cost of MRI follow-up was $14,185 with a health benefit of 24.02 quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs) in the base case of a 40-year-old patient; the cost of no follow-up was $1,059 with a health benefit of 24.11 QALYs. No follow-up was shown to be the better strategy in all 10,000 iterations in probabilistic sensitivity analysis. When the negative predictive value of the initial CT was relatively high (>98 percent), or the risk of an injury treated with a cervical collar turning into a permanent neurologic deficit was higher than 25 percent, or when the risk of a missed injury turning into a neurologic deficit was less than 58 percent, no follow-up was the better strategy.
"Magnetic resonance imaging had a lower health benefit and a higher cost compared with no follow-up after a normal CT finding in patients with obtunded blunt trauma to the cervical spine, a finding that does not support the use of MRI in this group of patients," the authors write.
More information:
Abstract/Full Text (subscription or payment may be required)
Editorial (subscription or payment may be required)
Copyright © 2018 HealthDay. All rights reserved.