Watching stem cells repair spinal cord in real time
Monash University researchers have restored movement and regenerated nerves using stem cells in zebra fish where the spinal cord is severely damaged.
The research, presented at the International Society for Stem Cell Research conference in Melbourne this week, raises the possibility that these same stem cells could be triggered in human patients who have suffered paralysing damage to their nervous system.
Dr. Jan Kaslin from Monash University's Australian Regenerative Medicine Institute (ARMI), used the zebra fish model of nerve regeneration.
Zebrafish are small, tropical fish that are known as "master-regenerators" because they have the capacity to regenerate many tissues or organs following injury, and being see-through scientists can literally watch the regeneration within the living fish.
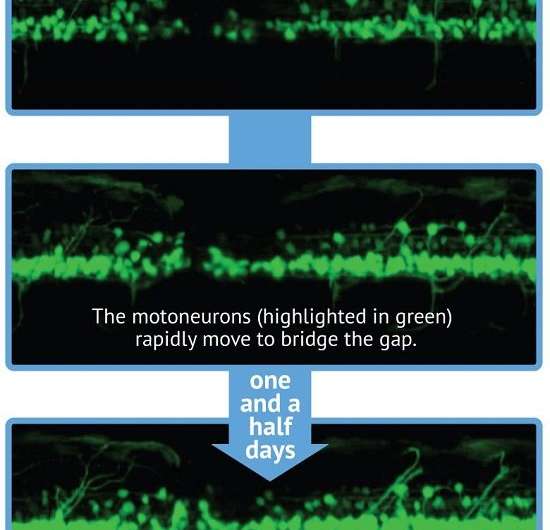
Dr. Kaslin and colleagues isolated a group of precursor cells and stem cells that very quickly colonise and regenerate the fish's spinal cord when it is damaged. Using confocal and light sheet microscopy Dr. Kaslin and colleagues were able to track and image the regeneration of living nerves in real time – allowing the first glimpse into how these precursor and stem cells move, behave and repair the spinal cord.
Dr. Kaslin has been able to watch, and film, the rapid process – which can take as little as two days to restore movement in zebra fish larvae and within 2-4 weeks in the adults.
"It's remarkable how quickly these fish regain their capacity to swim after injury," Dr. Kaslin said.
The researchers identified two "waves" of cell regeneration: the migration of neural precursors to the injury – which led to rapid recovery of movement – followed by the activation of stem cells in areas surrounding the injury site.
He added that by studying the genes and molecules involved in the recruitment of these remarkable stem cells to the injured nerve cord.
"It may be possible to learn how to turn these same switches on in humans who have had spinal cord or brain injury," Dr. Kaslin said.
The study opens the way to learning how to trigger the central nervous system in humans to regenerate, according to Dr. Kaslin.