Researchers identify common molecular mechanism in two skeletal disorders
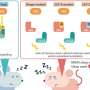
A rare and as-yet-unnamed skeletal disorder shares a common "signaling pathway" with another rare skeletal disorder called Jansen metaphyseal chondrodysplasia. (A signaling pathway is a group of molecules in a cell that work together to control one or more cell functions.) The findings point to the mechanisms that control both normal and disordered development of the skeleton, and could even lead to a novel target for cancer drugs.
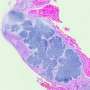
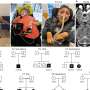
Skeletal disorders, or dysplasias—such as brittle bones or very short limbs—can arise from genetic mutations that affect the development of cartilage and bone. The researchers analyzed the genes of two children who are siblings who had a previously uncharacterized disorder that affects bone development as well as neurological and immune system development. The investigators wanted to determine whether the disorder shared genetic similarities with Jansen metaphyseal chondrodysplasia, or JMC. Both disorders cause similar changes in the bones.
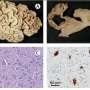
Analyzing the genetics of the siblings and their family, the team found that a homozygous mutation—an alteration that occurred in the copies of a gene each child inherited from each parent—of a protein called SIK3 was responsible for the siblings' disorder. The siblings' cells had a 60 percent reduction in SIK3 levels. But the siblings' parents and their brother, all of whom are unaffected by the disorder, each only had one copy of the mutation.
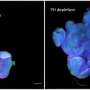
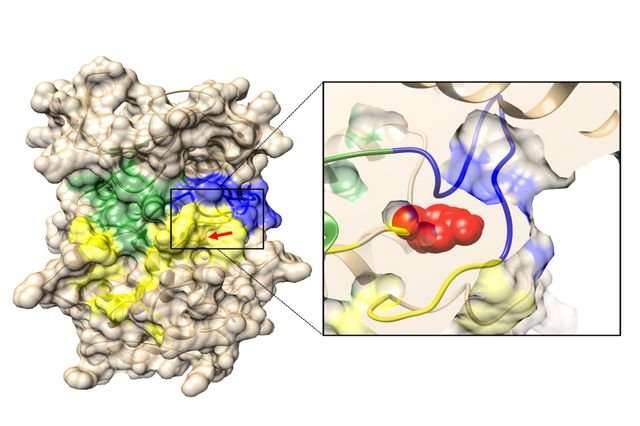
The researchers discovered that the reduction in SIK3 affects a pathway called mTOR, which functions as a sensor for the cellular environment, including nutrients and growth factors, and which helps regulate cell metabolism, growth and proliferation. The researchers also illustrated that a patient with JMC had decreased levels of active SIK3 and altered mTOR signaling—which supports the idea that reduced SIK3 levels are responsible for disruption in normal bone cell growth.
The fact that two related but distinct skeletal disorders share a common pathway helps explain the molecular mechanisms that control both normal and disordered skeletal development. The involvement of mTOR is important, because its degradation is known to be linked to various diseases, including diabetes and cancer. Because it can alter mTOR activity, SIK3 could be a possible target for new drugs.
The study was published in Science Translational Medicine.
More information: Fabiana Csukasi et al. The PTH/PTHrP-SIK3 pathway affects skeletogenesis through altered mTOR signaling, Science Translational Medicine (2018). DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aat9356