Exome sequencing provides genetic diagnosis for some with CKD
(HealthDay)—Genes are responsible for approximately one in 10 cases of chronic kidney disease in adults, according to a study published online Dec. 26 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Emily E. Groopman, from Columbia University in New York City, and colleagues conducted exome sequencing and diagnostic analysis for 3,315 patients with chronic kidney disease (two cohorts). A total of 3,037 patients were over age 21 years and 35.6 percent were self-identified as non-European ancestry.
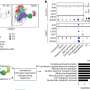
The researchers detected diagnostic variants in 9.3 percent of patients, encompassing 66 different monogenic disorders. Overall, 59 percent of the disorders detected were found in only a single patient. Across all clinically defined categories, diagnostic variants were detected, including congenital or cystic renal disease (23.9 percent of 531 patients) and nephropathy of unknown origin (17.1 percent of 281 patients). Overall, 1.6 percent of the 2,187 patients assessed had genetic findings for medically actionable disorders that would lead to subspecialty referral and inform renal management, even though they were unrelated to nephropathy.
"Our findings support the diagnostic utility of exome sequencing across different clinical categories of kidney disease and highlight the potential of genetic testing to accurately direct patients to relevant clinical trials and targeted therapies, encouraging similar investigations across other subspecialties," the authors write.
Several authors are employees of AstraZeneca, which partially funded the study.
More information: Abstract/Full Text (subscription or payment may be required)
Copyright © 2018 HealthDay. All rights reserved.