Surge protector: A novel approach to suppressing therapy-induced tumor growth and recurrence
Following up on a groundbreaking 2018 study in which BIDMC's Dipak Panigrahy, MD, demonstrated that dead and dying cancer cells killed by conventional cancer treatments paradoxically trigger inflammation that promotes tumor growth and metastasis, a new study led by Allison Gartung, Ph.D., describes a novel approach to suppressing chemotherapy-induced tumor growth in an ovarian cancer model. Gartung and colleagues' findings were published in published in January in Proceedings of the National Academy of Science (PNAS).
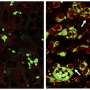
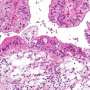
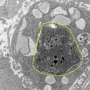
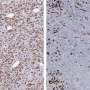
Working in a mouse model of the disease, the team confirmed that chemotherapy-killed ovarian cancer cells induce surrounding immune cells called macrophages to release a surge of chemicals. Together, these chemicals, known as cytokines and lipid mediators, create an environment conducive to tumor growth and survival.
"Conventional cancer therapy is a double-edged sword—the very treatment meant to control cancer is also helping it to survive and grow," said Gartung, a postdoctoral fellow in BIDMC's Department of Pathology. "To prevent tumor recurrence after therapy, it is critical to neutralize the inherent tumor-promoting activity of therapy-generated debris."
Next, the team showed that a newly synthesized anti-inflammatory drug called PTUPB—specifically designed to target the chemical pathways that lead to cytokines and lipid mediators—blocks the debris-stimulated surge of tumor-promoting chemicals by macrophages. In addition, the scientists found that PTUPB prolonged survival in mice bearing ovarian tumors and suppressed debris-stimulated tumor growth.
"The role of these chemotherapy-induced cytokines and lipids is underappreciated and poorly characterized, and ovarian cancer patients may benefit from suppressing their release," said Panigrahy, Assistant Professor of Pathology and a Scientist at the Cancer Center at BIDMC. "Further research is needed but, our results indicate that PTUPB may compliment conventional cancer therapies by acting as a 'surge protector' against cell debris-stimulated tumor growth."
More information: Allison Gartung el al., "Suppression of chemotherapy-induced cytokine/lipid mediator surge and ovarian cancer by a dual COX-2/sEH inhibitor," PNAS (2018). www.pnas.org/cgi/doi/10.1073/pnas.1803999116