Scientists believe it may be possible to reverse the heart damage caused by aging
New research, which has been published today in the EMBO Journal, could suggest a new way of preventing heart failure in older patients.
Heart failure occurs when the heart is not pumping blood around the body as well as it should, most commonly when the heart muscle has been damaged – for example, after a heart attack.
Risk of heart failure
aging is one of the main risk-factors for heart failure, as older people are more likely to develop heart disease and don't recover as well following a heart attack.
This research, carried out in mice, was led by Dr. Gavin Richardson, Dr. Jeanne Mialet-Perez and Dr. Joao Passos, and funded by the British Heart Foundation.
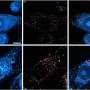
It explores how senescent cells – also known as zombie cells – form in the heart and lead to heart failure.
Zombie cells occur all over the body as it ages. They get their nickname from the fact that although they are not dead they do not function correctly and can cause other cells around them to become senescent (or zombiefied)
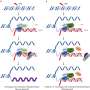
Elsewhere in the body, zombie cells are usually caused by the shortening of structures called telomeres, which happens progressively each time a cell divides. But the as heart cells – cardiomyocytes – rarely divide it was not known if or how these cells could become senescent.
The Newcastle scientists, in collaboration with researchers in the US and France, have not only discovered how this process takes place in the heart but also how it can be reversed or treated.
Dr. Richardson, from the Institute of Genetic Medicine, Newcastle University, said: "Previously, it was believed that senescence occurs only as a result of a lifetime of cell division and the shortening of telomeres.
"Our data support the very exciting idea that heart cells can become senescent due to stress rather than the process of division. This mechanism could also explain how other non-dividing cells in our bodies age.
"We saw that removing senescent cardiomyocytes from the hearts of aged mice, both genetically and using drugs, was able to restore cardiac health – essentially removing the damage caused by aging.
"This data provides critical support for the potential of using medicines to kill zombie cells. If this is validated through clinical trials it would provide us with a new way of treating cardiac diseases."
Healthy aging
More than 580,000 people in the UK are on their GP's heart failure register.
Based on this research, the team is now exploring the effects of removing senescent cells found as a consequence of a heart attack.
Jeremy Pearson, BHF Associate Medical Director, said: "People are living longer lives, but often as they get older, their health deteriorates and their quality of life is negatively affected.
"This research is exciting because it could potentially help us to tackle the increasing numbers of people with heart failure, meaning that elderly people could stay well for longer, and continue to lead full and active lives.
"The research is still in its early stages, but this study funded in part by the generous donations of BHF supporters, could be the first step towards a new era for healthy aging."
More information: Rhys Anderson et al. Length‐independent telomere damage drives post‐mitotic cardiomyocyte senescence, The EMBO Journal (2019). DOI: 10.15252/embj.2018100492