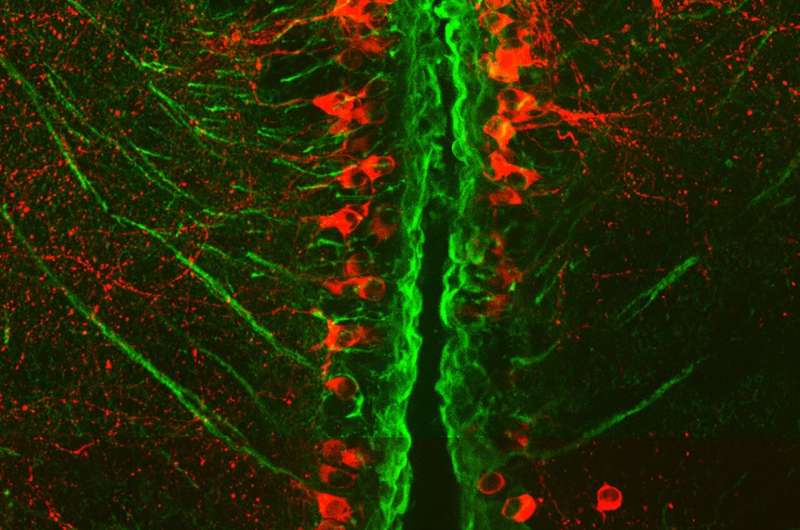
Research using zebrafish has revealed how key brain cells that are damaged in people with Parkinson's disease can be regenerated. In this microscope picture of a zebrafish brain, dopamine-producing nerve cells are shown in red and the stem cells that produce them are shown in green. Credit: Thomas Becker, The University of Edinburgh
Parkinson's patients could be helped by fresh insights gained from studies of tiny tropical fish.
Research using zebrafish has revealed how key brain cells that are damaged in people with Parkinson's disease can be regenerated.
The findings offer clues that could one day lead to treatments for the neurological condition, which causes movement problems and tremors.
Parkinson's occurs when specialised nerve cells in the brain are destroyed. These cells are responsible for producing an important chemical called dopamine.
When these cells die, or become damaged, the loss of dopamine causes body movements to become impaired. Once these cells are lost from the human brain, they cannot be repaired or replaced.
In zebrafish, however, dopamine-producing nerve cells are constantly replaced by dedicated stem cells in the brain, the researchers found.
The team, led by the University of Edinburgh, found the immune system plays a key role in this process. In some regions of a zebrafish's brain, the process does not work, however.
Researchers say understanding the immune signals that facilitate replacement of these nerve cells could hold vital clues to developing treatments for people.
The study, published in the Journal of Neuroscience, was funded by the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council and the Medical Research Council.
Dr. Thomas Becker, of the University of Edinburgh's Centre for Discovery Brain Sciences, said: "We were excited to find that zebrafish have a much higher regenerative capacity for dopamine neurons than humans. Understanding the signals that underpin regeneration of these nerve cells could be important for identifying future treatments for Parkinson's disease."
More information: Journal of Neuroscience (2019). DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2706-18.2019
Journal information: Journal of Neuroscience
Provided by University of Edinburgh