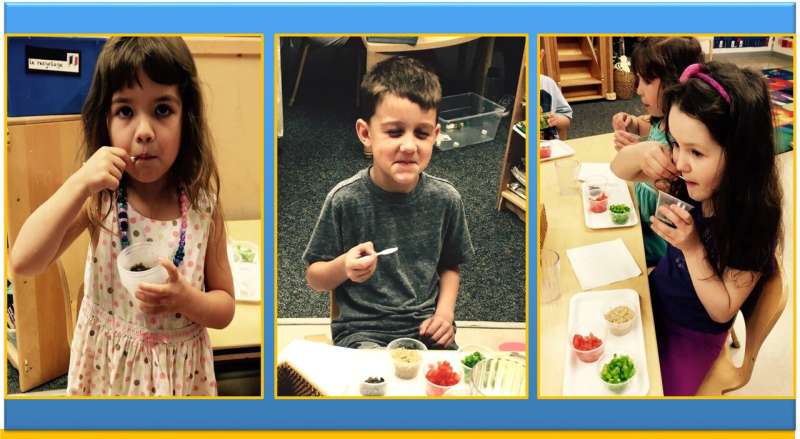
Lanigan and her colleagues ran a series of experiments offering healthy foods to a group of three- to-five-year-old children for seven weeks. Credit: WSU
Communicating food benefits to children that they can relate to may get them to eat healthier.
That's according to a study published today in the Journal of Nutrition Education and Behavior by Washington State University and Florida State University scientists.
The researchers found affirming statements like 'eat your lentils if you want to grow bigger and run faster' were more effective at getting kids to make healthy food choices than presenting the food repeatedly without conversation.
In fact, kids ate twice as much healthy food when they were told how it would benefit them in terms they could understand as opposed to when they were given the food with no contextual information.
"Every child wants to be bigger, faster, able to jump higher," said Jane Lanigan, associate professor in the WSU Department of Human Development and lead author of the study. "Using these types of examples made the food more attractive to eat."
Previous research shows that offering foods repeatedly increases the likelihood that kids will try something new. But that research didn't look at the context of those offerings, Lanigan said.
Examples of phrases used to encourage kids to eat healthy. Credit: WSU
In their study, Lanigan and her colleagues wanted to see if child-centered nutrition phrases (CCNPs), affirmative statements that simply convey the benefits of healthy food, influenced young children to make healthier food choices. The phrases focus on goals children have and are based on accurate nutrition information.
The WSU and FSU research team ran an experiment where they offered healthy foods to a group of three-to-five-year old children for six weeks.
Before beginning, the 87 children in the experiment ranked how much they liked four foods chosen from different food groups including, green peppers (vegetable), tomatoes (vegetables), quinoa (grain), and lentils (protein).
The kids were then offered two of the foods they liked the least twice a week. Over the six-week experiment, the researchers presented the children one of their low-rated foods with pre-selected age-appropriate facts about the benefits of the food. The other food was merely given to them to taste. A coin flip determined which food would be paired with the CCNP. The experiment was built into the kids' normal class routine, Lanigan said.
The researchers then measured how much the kids ate at three times: pre-test, post-test, and one month after the study ended. The immediate post-test showed no result, likely because the kids "got sick of eating the same foods," Lanigan said.
Jane Lanigan, PhD, discusses a new study in the Journal of Nutrition Education and Behavior that shows that child-centered nutrition phrases encourage healthy eating, especially when introducing new foods. They found that repeated opportunities for children to become familiar with the food without pressure helped them understand the benefits of healthy eating and increased consumption. Credit: Journal of Nutrition Education and Behavior
Results and impact
The month-after measurement told a different story.
"We found that a month later, the kids ate twice as much of their CCNP food with the repeated exposure compared to the food without the positive words," Lanigan said. "For example, when we presented lentils we would say, 'This will help you grow bigger and run faster."
Over time, Lanigan and colleagues' study shows that using CCNPs is likely to increase the amount of healthy food that children eat.
"I have two kids and I probably could have done things differently when trying to get them to eat healthier," Lanigan said. "We wanted to fill a gap, where parents are often told what their kids should be eating but not how to get them to eat it. And that's really important."
More information: Journal of Nutrition Education and Behavior (2019). DOI: 10.1016/j.jneb.2019.02.011
Journal information: Journal of Nutrition Education and Behavior
Provided by Washington State University