Credit: CC0 Public Domain
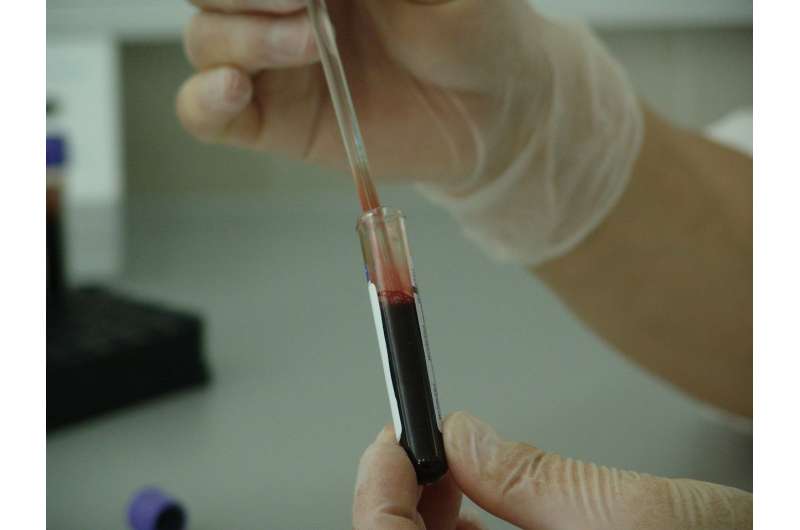
A new Murdoch Children's Research Institute study has highlighted the challenges of consistently diagnosing child blood samples and sourcing healthy samples for research. Published in Clinical Chemistry, the research paper, "Pediatric reference intervals across 5 analyzers," used the blood samples of 616 healthy children and found that results from different laboratories were not always uniform.
MCRI's co-group leader of hematology research and University of Melbourne Associate Professor Vera Ignjatovic says laboratories test whether levels of blood biomarkers (like sodium and potassium) are within a normal range but defining normal can be difficult, especially when it comes to children.
"To define a normal range you need to test the blood of a large group of people," says A/Prof Ignjatovic.
"Getting access to the blood of healthy people can be problematic, especially when it comes to children and newborns. While parents are generally not reluctant to get their children to donate blood for research, children can only donate small amounts of blood, a factor that can create difficulties."
A/Prof Ignjatovic said that variations in results were either due to differences in how the blood was tested or because specific blood reference values for children are needed.
"Better reference intervals (which define the normal range) could help improve clinical decisions in children around the world. Clinical laboratory test results are critical to evidence-based medicine, with nearly 80 percent of physicians' decisions based on information provided by laboratory reports."
The study examined the results of tests for 30 blood biomarkers produced by five different automated blood analyzing machines.
"Results from the five analyzers were mostly within the 'allowable error' margin, however there were some variation," A/Prof Ignjatovic said.
"For creatinine, a waste product produced by muscles, levels varied by 11.9 percent between machines. Whether patient samples tested at different laboratories, using different analyzing machines, can be directly compared is of global importance.
A/Prof Ignjatovic says that lack of regulatory incentives for manufacturers of lab machines may be contributing to lack of data on pediatric specific reference intervals and that changes to regulations could facilitate improvements in availability of age-specific reference ranges.
"This would help improve clinical result interpretation and decision making," she says.
Lead author of the paper, MCRI researcher, Monsurul Hoq, says the need for consistent blood diagnosis is even more crucial when a child's care is shared by a specialist, central hospital and local health care providers.
For the study, blood was taken from 616 child participants aged a few hours old to 17 years. Of the 30 blood biomarkers assessed, results varied statistically and clinically for six of the 30.
A/Prof Ignjatovic and Mr Hoq have called for more research in the area.
Until now no study has compared the reference values obtained by testing samples from same individuals on five analyzer machines using blood samples from healthy newborns and children.
The child participants are part of the Harmonizing Age Pathology Parameters in Kids (HAPPI Kids) study—a prospective, cross-sectional study of pediatric blood samples for commonly requested biomarkers.
Journal information: Clinical Chemistry
Provided by Murdoch Children's Research Institute