Credit: CC0 Public Domain
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and other stress related disorders are associated with a subsequent risk of life threatening infections such as meningitis and sepsis, finds a large Swedish study published in The BMJ today.
The risk was particularly high among people diagnosed at a younger age and those with other psychiatric conditions.
Despite a relatively low absolute risk for individuals, the high mortality from these infections calls for increased clinical awareness among health professionals caring for patients with stress related disorders, especially those diagnosed at a younger age, say the researchers.
Stress related disorders—severe conditions triggered by a significant life event or trauma—are common and linked to poor mental and physical health.
In a similar study published earlier this year, the authors found a link between stress related disorders and risk of cardiovascular disease.
Evidence also suggests that psychological stress might increase susceptibility to infections through reduced immunity, but data on major life threatening infections, such as sepsis and meningitis, are limited.
To address this knowledge gap, a team of international researchers used Swedish population and health registers to assess whether severe psychiatric reactions to trauma and other adversities are associated with subsequent risk of life threatening infections.
They compared infection rates for 144,919 patients diagnosed with a stress related disorder (PTSD, acute stress reaction, adjustment disorder, and other stress reactions) with 184,612 unaffected full siblings of these patients and a further 1,449,190 unaffected individuals from the general population.
Infections included sepsis, endocarditis (infection of the inner lining of the heart), and meningitis or other central nervous system infections.
Average age at diagnosis of a stress related disorder was 37 years and participants were monitored for an average of eight years.
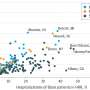
During follow-up, new cases of life threatening infections per 1000 person years was 2.9 in patients with a stress related disorder compared with 1.7 in unaffected siblings and 1.3 in unaffected individuals from the general population.
After controlling for family history and other physical or psychiatric conditions, stress related disorders were associated with all studied infections, with the highest relative risks found for meningitis (63% increased risk) and endocarditis (57% increased risk) compared with unaffected siblings.
Younger age at diagnosis and presence of other psychiatric conditions, especially substance use disorders, were associated with further risk increases, whereas use of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRI) antidepressants in the first year after diagnosis appeared to have a protective effect.
This is an observational study, so can't establish cause, and the researchers are unable to rule out the possibility that other unmeasured factors may have influenced their results.
However, they point out that their findings were largely unchanged after further analyses, and are in line with previous studies on the biological link between stress and infection.
As such they call for increased awareness among health professionals caring for patients with stress related disorders, especially those diagnosed at a younger age.
And they say further studies are needed to better understand the roles of lifestyle factors as well as treatments for stress related disorders in reducing the excess risk of life threatening infections.
The true nature of the relation between physical health and stress related disorders is difficult to tease out, but various biological, psychological, and social factors are likely contributors, explains Professor Jonathan Bisson from Cardiff University, in a linked editorial.
This study adds to previous research suggesting "overlapping mechanistic pathways between mental and physical health," he writes. As such, he believes a holistic approach to research and management of stress related disorders, in partnership with patients and families, is likely the best way to help people with this common and debilitating condition.
More information: Stress related disorders and subsequent risk of life threatening infections: population based sibling controlled cohort study, The BMJ, DOI: 10.1136/bmj.l5784
Provided by British Medical Journal